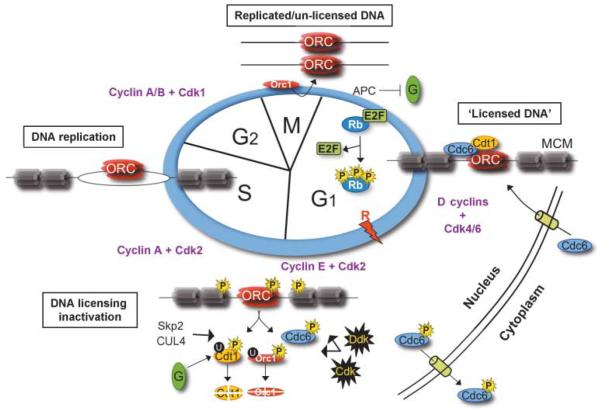
Figure 2.
Mammalian pre-RC formation and DNA licensing in the context of cell cycle progression. In early G1, cyclin D-cdk4/6 phosphorylation of Rb, which permits E2F transcriptional activity, triggers entry into the cell cycle. Pre-RCs form via stepwise binding of licensing factors Orc1–6, Cdc6, Cdt1, and Mcm2–7, required for DNA licensing. Progressing into S-phase, CDK, and DDK phosphorylation of pre-RC constituents initiates Orc1 dissociation, and the removal and subsequent nuclear export of Cdc6, while geminin, along with CDK and DDK activity, trigger the removal and degradation of Cdt1. This regulation serves to ‘un-license’ the DNA and prevents re-licensing before completion of the initiated cell cycle. E2F target genes: Cdc6, MCM, Dbf4 (DDK), Cyclins E, and A. SCFSKP2, Skp1-cullin-F box E3 ubiquitin ligase; CUL4, CUL4-DDB1-CDT2 ubiquitin ligase; R, restriction point; G, geminin; U, ubiquitin; P, phosphate.