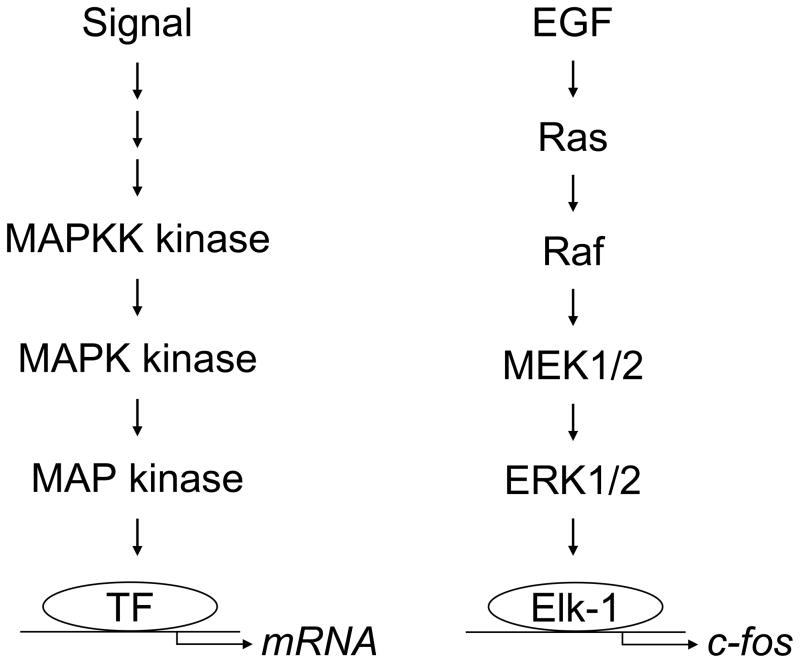
Fig. 1.
MAP kinases are regulated by protein kinase cascades. The cell receives a signal that stimulates the activation of a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAPKK kinase). The MAPKK kinase then phosphorylates and activates a MAP kinase kinase (MAPK kinase or MEK). The MAPK kinase then phosphorylates and activates a MAP kinase. The phosphorylated, active MAP kinase can translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and then phosphorylate and activate transcription factors (TF), resulting in changes in gene expression. For example, EGF stimulates the activation of the GTPase Ras. Ras activates Raf (a MAPKK kinase). Raf phosphorylates and activates MEK1/2 (the MAPK kinases MEK1 and MEK2). MEK1/2 phosphorylates and activates ERK1/2 (MAP kinases). ERK1/2 can then translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus to phosphorylate transcription factors such as Elk-1, which regulates the expression of c-Fos.