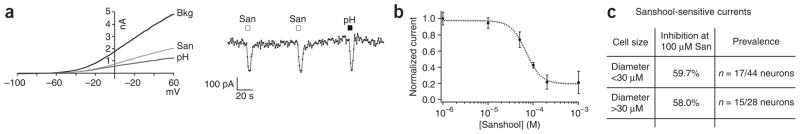
Figure 2.
Sanshool inhibits pH-sensitive background potassium channels in sensory neurons. (a) Representative whole-cell voltage-clamp recording from a cultured trigeminal neuron subjected to a voltage ramp (+60 mV to −100 mV, 100 ms; applied every 2 s). Current-voltage relationship before (Bkg) or after application of sanshool (100 μM) or low pH (pH 6.5) (left). Average current recorded at −60 mV in response to sanshool or low pH (right). (b) Dose-response curve of sanshool-evoked inhibition of background potassium conductance in sensory neurons (holding potential = –60 mV) recorded in extracellular Ringer’s solution (IC50 = 69.5 ± 5.3 μM; n = 3–7 cells per point). (c) Summary of sanshool-sensitive currents measured in small- and large-diameter neurons.