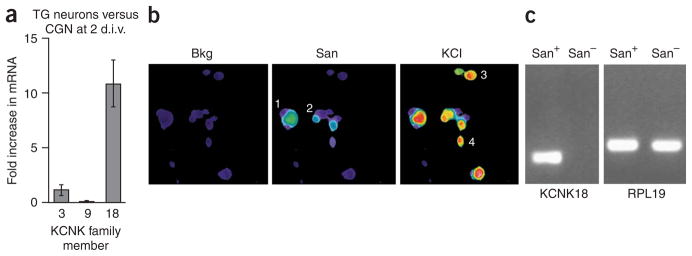
Figure 6.
Sanshool excites sensory neurons that express KCNK3, KCNK9 or KCNK18. (a) Quantitative PCR analysis of sanshoolsensitive KCNK expression in cultured trigeminal (TG) sensory neurons versus CGN cultured for 2 d.i.v. (n = 3–4). (b) Representative calcium imaging experiment used to identify sanshoolsensitive cells. Cells 1 and 2 are sanshoolsensitive, whereas cells 3 and 4 are insensitive. (c) Representative PCR analysis of KCNK18 expression in sanshool-positive and sanshoolnegative sensory neurons. Lane 1 contains a sample amplified from cDNA prepared from cells 1 and 2; lane 2 contains a sample amplified from cDNA prepared from cells 3 and 4 (see above). n = 6 samples for sanshool-sensitive neurons and 3 for sanshool-insensitive neurons; each sample contained 2–3 cells. Note the presence of control RPL19 product in all samples (right).