Figure 7.
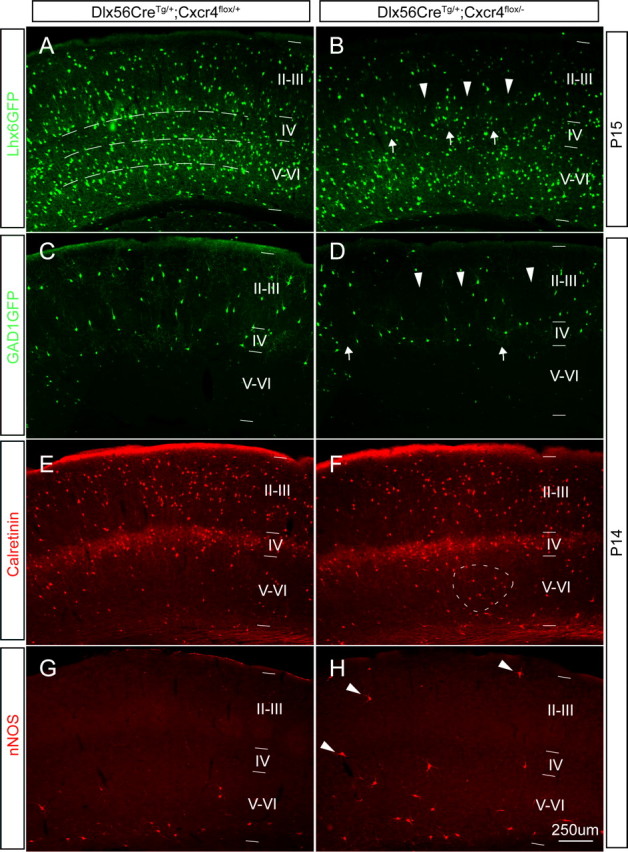
Postnatal conditional Cxcr4 mutants have subtle defects in interneuron positioning. A–D, One copy of the Lhx6-GFP BAC transgene or GAD1GFP transgene was crossed into the control background Dlx5/6CreTg/+;Cxcr4flox/+ (A, C) or the conditional mutant background Dlx5/6CreTg/+;Cxcr4flox/− (B, D). The distribution of GFP+ cells is shown in coronal sections from P14 or P15 animals. In both control and mutant animals, Lhx6-GFP+ cells were primarily localized in the deep layers, whereas GAD1-GFP is found mainly in the superficial layers (A–D). In the somatosensory cortex of the control animals, Lhx6-GFP+ cells showed three relatively distinct laminar concentrations from layer VI to IV, (indicated by the dotted lines in A). However, in Dlx5/6-cKO mutants, the Lhx6-GFP+ cells are distributed as clusters in layer V, and there are bare patches lacking labeled cells in layer IV (B, arrows and arrowheads). Similarly, GAD1-GFP+ cells are distributed quite evenly in the superficial cortex of controls (C), but there are again bare patches seen in the Dlx5/6-cKO mutants (D, arrowheads) and some areas of clustering (D, arrows). The interneuron subtype markers calretinin and nNOS also are useful to marker particular layer distributions in controls (E, G) and Dlx5/6-cKO mutants (F, (H). Most calretinin+ cells are localized in superficial region in both controls and Dlx5/6-cKO mutants, but the smaller fraction of calretinin+ cells in deeper regions is more evenly distributed in the controls (E), than in the Dlx5/6-cKO mutants, which have areas of clustered, labeled cells (F, dotted oval area). nNOS+ cells are primarily found in layer VI in both controls and Dlx5/6-cKO mutants, but there is a very reproducible finding of small numbers of nNOS+ interneurons straying into more superficial positions in the Dlx5/6-cKO mutants (H, arrowheads). Scale bar, 250 μm.
