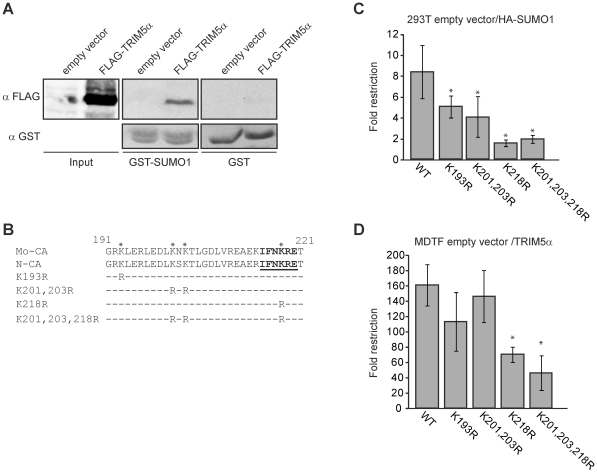
Figure 7. CA mutations altering putative SUMO conjugation site reduce SUMO-1 and TRIM5α-mediated restriction.
A. The ability of human TRIM5α to interact with SUMO-1 is shown by GST-pulldown. 293T cell were transiently transfected with an empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding a FLAG-tagged version of human TRIM5α, forty-eight hours after transfection total extract were prepared and assayed for interaction with GST or GST-SUMO1 produced in bacteria. Input corresponds to 5% of the amount used in the interaction assay. B. Amino acid sequence of the UBC9 binding region of CA protein. The lysine residues conserved between Mo-CA and N-CA are highlighted, and the consensus binding sequence is underlined. The position and identity of the substituted amino acids in N-CA are indicated for each mutant. C. The 293T empty vector and HA-SUMO-1 cell lines were infected with wild type N-MLV luc or N-CA mutant viruses. D. MDTF empty vector and wild-type human TRIM5α cell lines were infected with wild-type N-MLV luc or the N-CA mutant viruses. Forty-eight hours after infection, luciferase activity was measured, and the fold restriction between the two cell lines was calculated for different experiments, presented as average fold restriction. Error bars indicate standard deviation among 6 different experiments. * indicates p<0.01.