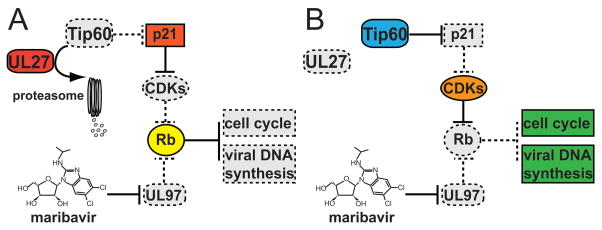
Figure 1. Model for the Roles of UL27 and the Tip60 Histone Acetyltransferase in Human Cytomegalovirus Antiviral Drug Resistance.
A) UL27 promotes proteasome-dependent degradation of Tip60, leading to increased expression of p21WAF/CIP(p21), an inhibitor of cellular cyclin-dependent kinase complexes (CDKs). Thus, in the presence of maribavir, an inhibitor of the UL97 protein kinase, wild-type human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) lacks any efficient mechanism, cellular or viral, by which to inactivate the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (Rb). Because active Rb represses cellular genes necessary for cell cycle progression and for viral DNA synthesis, wild-type HCMV replication is impaired in the presence of maribavir. B)UL27-null viruses are unable to promote degradation of Tip60. In the absence of Tip60 destruction, p21 expression remains low enough for cellular CDKs to inactivate Rb, thus compensating for maribavir inhibition of UL97 activity, and providing for resistance of UL27 mutant viruses to maribavir. In both A) and B), active functions are shown as solid-bordered, colored shapes, while inactive functions are shown as dashed-bordered, gray shapes.