Abstract
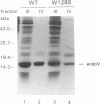
Endonuclease V of bacteriophage T4 possesses two enzymatic activities, a DNA N-glycosylase specific for cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CBPD) and an associated apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) lyase. Extensive structural and functional studies of endonuclease V have revealed that specific amino acids are associated with these two activities. Controversy still exists regarding the role of the aromatic amino acid stretch close to the carboxyl terminus, in particular the tryptophan at position 128. We have expressed wild-type and mutant W128S endonuclease V in Escherichia coli from an inducible tac promoter. Purified W128S endonuclease V demonstrated substantially decreased N-glycosylase (approximately 5-fold) and AP lyase (10- to 20-fold) activities in vitro compared to the wild-type enzyme when a UV-irradiated poly(dA)-poly(dT) substrate was used. However, a much smaller difference in AP lyase activity between the two forms was observed with a site-specific abasic oligonucleotide. The difference in enzymatic activity was qualitatively, but not quantitatively, reflected in the survival of UV-irradiated bacteria, that is the W128S cells were slightly less UV resistant than wild-type cells. No difference was observed in the complementation of UV repair using UV-damaged denV- T4 phage. A more pronounced difference between the wild-type and W128S proteins was observed in human xeroderma pigmentosum group A cells by host-cell reactivation of a UV-irradiated reporter gene. The relatively large discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo results observed with bacteria may be because saturated levels of DNA repair are obtained in vivo with relatively low levels of endonuclease V. However, under limiting in vitro conditions and in human cells in vivo a considerable difference between the W128S mutant and wild-type endonuclease V activities can be detected. Our results demonstrate that tryptophan-128 is important for endonuclease V activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behmoaras T., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. A tryptophan-containing peptide recognizes and cleaves DNA at apurinic sites. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):858–859. doi: 10.1038/292858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R., Cullen B. R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockrath R., Hodes M. Z., Mosbaugh P., Valerie K., de Riel J. K. UV mutagenesis in E. coli with excision repair initiated by uvrABC or denV gene products. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;193(2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowd D. R., Lloyd R. S. Biological consequences of a reduction in the non-target DNA scanning capacity of a DNA repair enzyme. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. K., Seawell P. C., Lewis R. J., Hanawalt P. C. Processivity of T4 endonuclease V is sensitive to NaCl concentration. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5751–5755. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruskin E. A., Lloyd R. S. The DNA scanning mechanism of T4 endonuclease V. Effect of NaCl concentration on processive nicking activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9607–9613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori N., Doi T., Karaki Y., Kikuchi M., Ikehara M., Ohtsuka E. Participation of glutamic acid 23 of T4 endonuclease V in the beta-elimination reaction of an abasic site in a synthetic duplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4761–4764. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L., Stedeford J. B. Some properties of excision-defective recombination-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1134–1141. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1134-1141.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida M., Kanamori Y., Hori N., Inaoka T., Ohtsuka E. In vitro and in vivo activities of T4 endonuclease V mutants altered in the C-terminal aromatic region. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3817–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Linn S. The mechanisms of action of E. coli endonuclease III and T4 UV endonuclease (endonuclease V) at AP sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1135–1141. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham K. A., Carmical J. R., Lloyd R. S. Mutation of tryptophan 128 in T4 endonuclease V does not affect glycosylase or abasic site lyase activity. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 2;33(30):9024–9031. doi: 10.1021/bi00196a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa K., Matsumoto O., Tsujimoto M., Katayanagi K., Ariyoshi M., Doi T., Ikehara M., Inaoka T., Ohtsuka E. X-ray structure of T4 endonuclease V: an excision repair enzyme specific for a pyrimidine dimer. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):523–526. doi: 10.1126/science.1575827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Physical association of pyrimidine dimer DNA glycosylase and apurinic/apyrimidinic DNA endonuclease essential for repair of ultraviolet-damaged DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2742–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Yamashita K., Sekiguchi M. Purification and characterization of normal and mutant forms of T4 endonuclease V. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2556–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radany E. H., Naumovski L., Love J. D., Gutekunst K. A., Hall D. H., Friedberg E. C. Physical mapping and complete nucleotide sequence of the denV gene of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):846–856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.846-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recinos A., 3rd, Augustine M. L., Higgins K. M., Lloyd R. S. Expression of the bacteriophage T4 denV structural gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1014-1018.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recinos A., 3rd, Lloyd R. S. Site-directed mutagenesis of the T4 endonuclease V gene: role of lysine-130. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1832–1838. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saporito S. M., Gedenk M., Cunningham R. P. Role of exonuclease III and endonuclease IV in repair of pyrimidine dimers initiated by bacteriophage T4 pyrimidine dimer-DNA glycosylase. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2542–2546. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2542-2546.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrock R. D., 3rd, Lloyd R. S. Site-directed mutagenesis of the NH2 terminus of T4 endonuclease V. The position of the alpha NH2 moiety affects catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stump D. G., Lloyd R. S. Site-directed mutagenesis of the T4 endonuclease V gene: role of tyrosine-129 and -131 in pyrimidine dimer-specific binding. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1839–1843. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toulmé J. J., Charlier M., Héléne C. Specific recognition of single-stranded regions in ultraviolet-irradiated and heat-denatured DNA by tryptophan-containing peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3185–3188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., Fronko G., Long W., Henderson E. E., Nilsson B., Uhlén M., de Riel J. K. Production and detection of coliphage T4 endonuclease V polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies using staphylococcal protein-A hybrid proteins. Gene. 1987;58(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., Green A. P., de Riel J. K., Henderson E. E. Transient and stable complementation of ultraviolet repair in xeroderma pigmentosum cells by the denV gene of bacteriophage T4. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2967–2971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., Henderson E. E., de Riel J. K. Expression of a cloned denV gene of bacteriophage T4 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4763–4767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., Henderson E. E., deRiel J. K. Identification, physical map location and sequence of the denV gene from bacteriophage T4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8085–8096. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., Singhal A. Host-cell reactivation of reporter genes introduced into cells by adenovirus as a convenient way to measure cellular DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1995 Jan;336(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(94)00046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner H. R., Christensen L. M., Persson M. L. Evidence that the UV endonuclease activity induced by bacteriophage T4 contains both pyrimidine dimer-DNA glycosylase and apyrimidinic/apurinic endonuclease activities in the enzyme molecule. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.204-210.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]