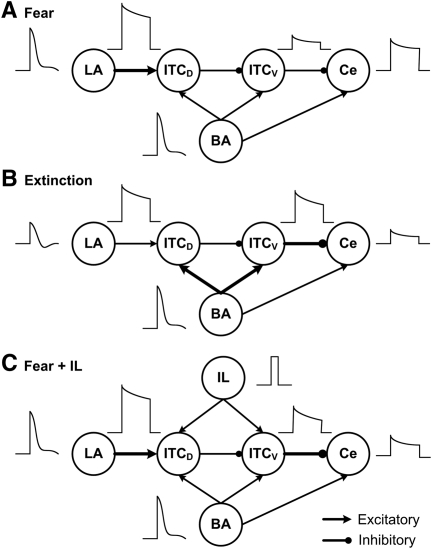
Figure 8.
Schematic illustrating the patterns of neuronal activity in the amygdala under different network situations. In the high fear state (A), the LA–ITCD connection strength is potentiated. Strongly adaptive LA inputs are transformed into much sustained output by ITCD neurons, leading to persistent inhibition on ITCV cells allowing for sustained Ce firing. In the extinction state (B), the LA inputs diminish and the LA–ITCD synapses depotentiate, while the BA–ITC synapses potentiate. Similarly, strongly adaptive BA inputs are transformed by ITCV neurons into sustained firing, leading to persistent inhibition of Ce output. When IL stimulation is given in the fear state (C), brief IL inputs increase the excitability of both ITCD and ITCV neurons, with a larger impact on ITCV cells, which significantly reduces the Ce firing. Note that the transmission efficiency (release probability) of the ITCV–Ce synapses is increased during extinction or with IL stimulation, enhancing inhibition on Ce output neurons.