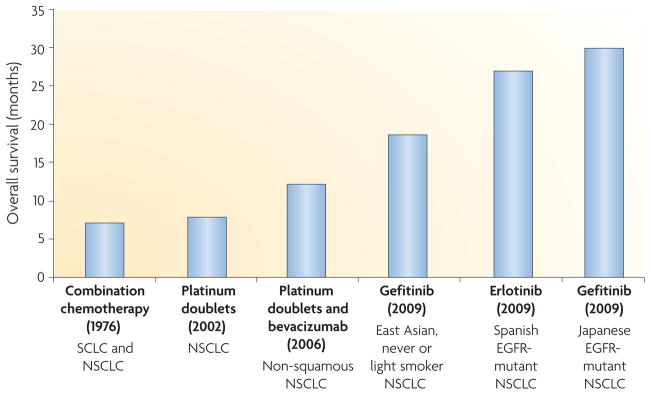
Figure 1. Progress in the treatment of metastatic lung cancer.
In 1976, a chemotherapy trial studied all patients with lung cancer, regardless of whether they had small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) or non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)3. In 2002, a landmark chemotherapy trial involving platinum doublets studied all patients with NSCLC, regardless of histological subtype (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large-cell carcinoma)152. In 2006, bevacizumab (Avastin; Genentech/ Roche) was shown to confer an overall survival benefit when added to chemotherapy for patients with non-squamous NSCLC153. The smoking history of patients was not recorded. In 2009, trials in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant lung cancer with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) demonstrated the longest survival rates currently seen for NSCLC20,21,47. Notably, patients with EGFR-mutant lung tumours also have a better prognosis in the absence of therapy compared with those with EGFR-wild-type tumours20.