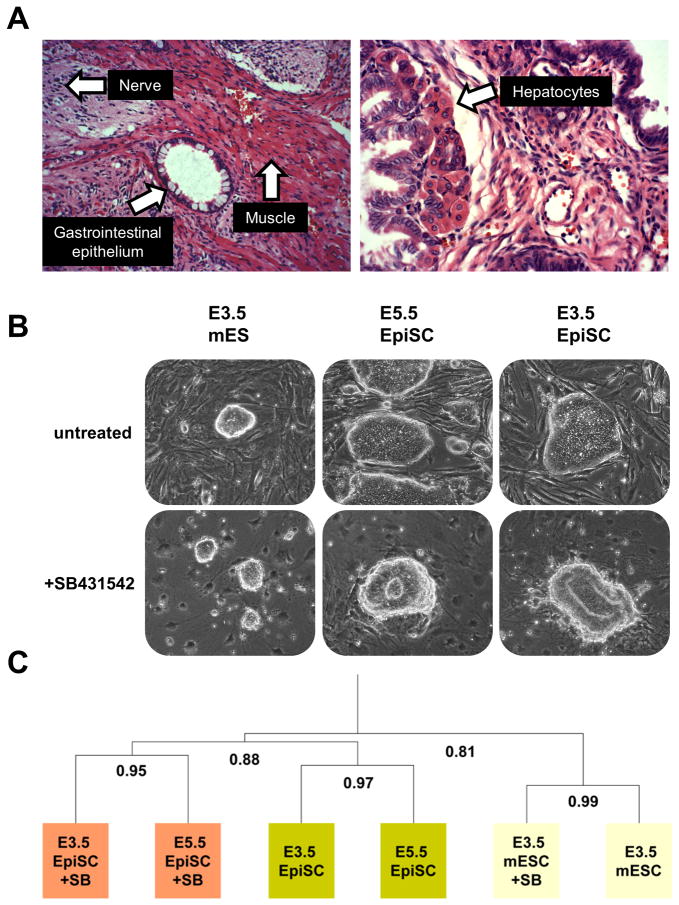
Figure 3. Pre- and post-implantation-derived EpiSCs utilize similar & developmentally-relevant mechanisms to regulate pluripotency and differentiation.
(A) Pre-implantation-derived EpiSCs are pluripotent as evidenced by haematoxylin and eosin stained histological sections of teratomas. Examples of specific cell types are denoted with an arrow. Additional images are found in Figure S1. Both pre- (E3.5) and post- (E5.5) implantation derived EpiSCs exited pluripotency and differentiated into neural rosettes in response to Alk-4/5/7 inhibition while mouse ES cells maintained their pluripotency as evidenced by (B) morphology and (C) hierarchical cluster analysis of whole genome microarray data of treated and untreated samples.