Figure 1.
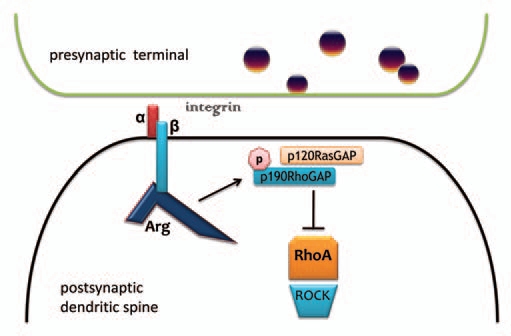
Arg interacts with β-integrin tails and p190RhoGAP to stabilize synapses, spines and dendrites. Arg is activated through a physical interaction with intracellular β-integrin tails, which allows for p190RhoGAP phosphorylation and recruitment to the membrane by p120RasGAP. This complex inhibits RhoA GTPase activity. In the absence of RhoA inhibition, RhoA acts on ROCK to destabilize the actin cytoskeleton, leading to spine and dendrite collapse and synapse loss. Conversely, ROCK inhibition elongates dendritic branches.47
