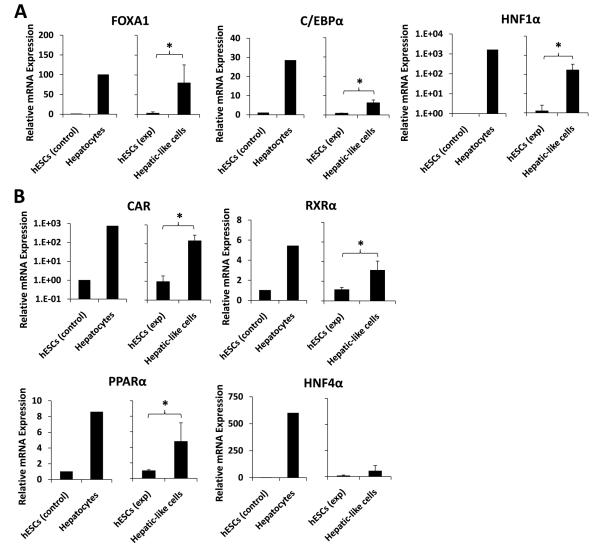
Figure 5. Hepatic transcription factor mRNA expression is increased in hepatic-like cells.
Passage-matched hESCs were cultured in parallel on either hFF feeder layers in hESC media (hESCs exp) or on collagen in hepatocyte media (Hepatic-like cells). After 10 days in culture, cells were harvested and RNA was isolated, converted to cDNA, subjected to real-time PCR, and the data analyzed using the ΔΔCT method [32] to determine fold expression levels relative to low-passage hESCs (hESCs control) of: (A), the hepatic transcription factors FOXA1, C/EBPα, and HNF1α; and (B), the hepatic nuclear receptors CAR, RXRα, PPARα, and HNF4α. Control data (left graph for each endpoint) depict means of expression levels of replicate determinations of a typical low-passage culture of hESCs (hESCs control), in contrast to mean expression levels of replicate determinations performed using a pooled sample of six adult primary human hepatocyte donors (Hepatocytes). In these control experiments, the replicate values were reproducible within a ≤ 5% error range. Experimental data (right graph) depict expression levels of hESCs (hESCs exp) and passage-matched hESCs subject to our hepatic differentiation protocol (Hepatic-like cells). Experimental data are expressed as mean +/− standard deviations of at least three independent trials using hESCs from different passages. * p < 0.05.