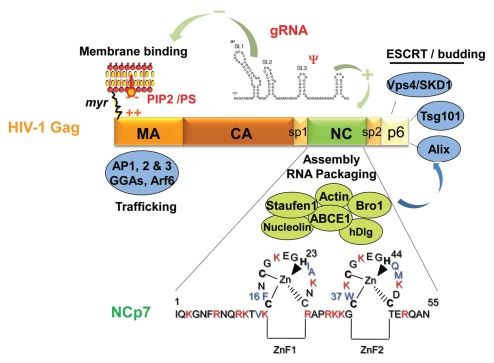
Figure 3.
The Gag polyprotein precursor, its NC domain and the associated cellular factors. HIV-1 Gag is composed of 3 main domains which are MA, CA and NC, one C-terminal peptide p6 and two spacer peptides, sp1 and sp2. The matrix MA domain is responsible for Gag membrane binding via the myristate and the basic (++) region with the PIP2/PS phospholipids. MA domain contains motifs that bind different cellular factors, such as AP1, AP2, AP3, GGA and Arf6 involved in Gag trafficking. The NC domain of Gag is necessary for gRNA recruitment via its interaction with the Psi packaging signal and the NC basic residues (in red) and the hydrophobic plateau encompassing the two conserved zinc fingers. The gRNA is also able to interact with the MA domain by competing with PI(4,5)P2. The NC domain is a key factor for the early assembly complex formation by Gag multimerization on the gRNA. NC and p6 interact with cellular factors; NC with actin, Staufen1, the Bro1 domain of ALIX and ABCE1 as described in this review; the C-terminus of Gag, via the p6 peptide containing the late budding domain is able to recruit the ESCRT cellular proteins, such as Tsg101, Alix and Vps4/SDK1, which are essential for particle budding. Sp1 and Sp2 are linker involved in HIV-1 morphogenesis. The 55 amino acids of mature NC are given; NCp7 is highly basic (in red) and contains two highly conserved zinc CCHC binding motifs and a plateau of hydrophobic amino-acids (in blue) involved in RNA-NC interactions, RNA chaperone activities and particle assembly.