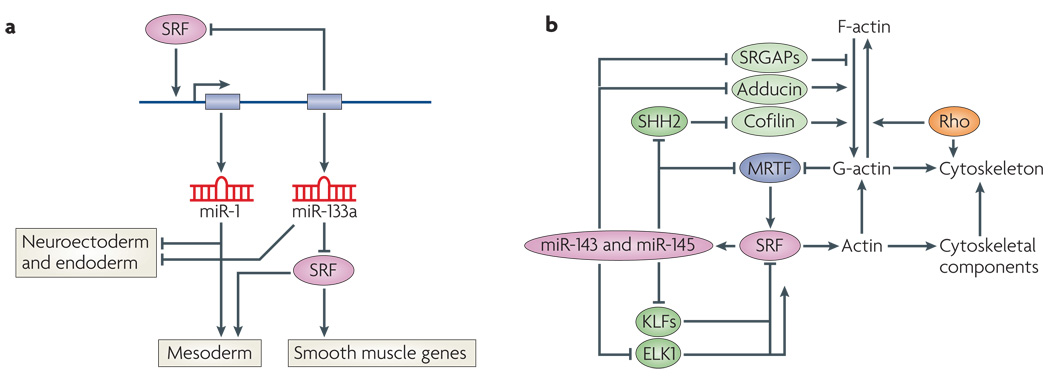
Figure 4. SRF-mediated regulation of miRNAs.
a | Regulation of microRNA-1 (miR-1) and miR-133 by sereum response factor (SRF). SRF activates transcription of a bicistronic miRNA cluster encoding miR-1 and miR-133 (REFS 112,113). miR-133a inhibits SRF expression, establishing a precisely titrated feedback loop to modulate SRF activity. There are two clusters of miR-1 and miR-133a genes in mammalian genomes, which are expressed specifically in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. A third homologous pair of miRNAs, miR-206 and miR-133b, is expressed specifically in skeletal muscle independently of SRF. Genetic deletion of miR-1 results in phentoypes that suggest it has a role in mesoderm formation. Genetic deletion of the two miR-133a genes results in perinatal lethality owing to cardiac defects. miR-1 and miR-133a also repress neuroectoderm and endoderm genes and promote mesoderm gene expression. miR-1 can substitute for SRF to regulate downstream genes involved in mesoderm development by an undefined mechanism. b | Regulation of miR-143 and miR-145 by SRF. SRF activates transcription of a bicistronic miRNA cluster encoding miR-143 and miR-145, which are expressed specifically in cardiac and smooth muscle cells115,117. These miRNAs, regulate the expression of numerous mRNAs encoding regulators of actin signalling and myocardin-related transcription factor (MRTF)–SRF activity, thereby establishing an elaborate series of feedback loops to modulate the actin–MRTF–SRF signalling pathway. Targets of miR-143 or miR-145 include the zinc-finger proteins krueppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) and KLF5 (which inhibit SRF), MRTF-B, slingshot 2 phosphatase (SHH2; which controls actin polymerization by cofilin phosphorylation), adducin 3 (which promotes actin polymerization) and Slit-Robo Rho GTPase-activating protein 1 (SRGAP1) and SRGAP2 (which inhibit Rho signalling)115. This pathway has been shown to be essential for vascular remodelling in response to injury. In the absence of miR-143 and miR-145, actin stress fibre formation is disrupted, rendering smooth muscle cells insensitive to mechanical stimuli that typically cause vascular stenosis.