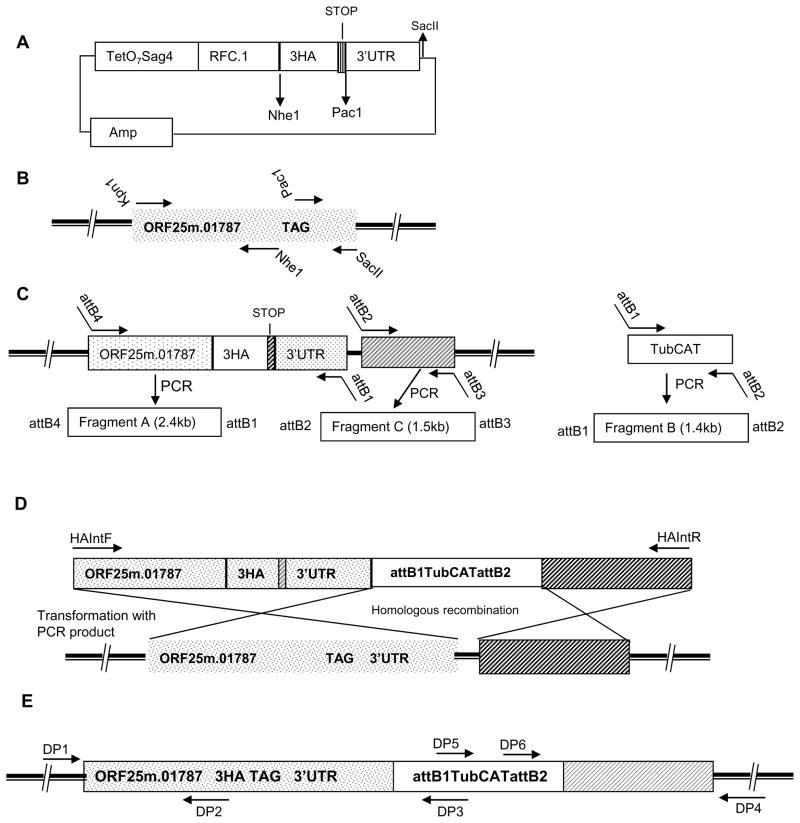
Figure 1. Design of a Gateway epitope tagging vector for T. gondii and the strategy for chromosomal C-terminal epitope tagging of ORF25.m01787.
A: Schematic map of the Gateway plasmid pTetO7SAG4RFC.13HA: Various restriction sites present in the fragments RFC.1 and TetO7SAG4 and the vector backbone can be used for target gene cloning. Multiple restriction sites are available in the vector after SacII for cloning the 3’UTR of the target gene.
B: Cloning of part of ORF25.m01787 genomic region into pTetO7SAG4RFC.13HA vector to generate a C-terminal epitope tag fusion: Location of the primer in the genomic region of ORF25.m01787 used for epitope insertion and cloning to pTetO7SAG4RFC.13HA vector. Solid dark bar represents chromosome.
C: Generation of gateway entry vectors: Location of the attB hybrid PCR primers designed to amplify PCR fragments for BP clonase mediated generation of three entry vectors. Each PCR fragment is flanked with unique attB sequences that are designed for the three fragment multisite Gateway® reaction.
D: Structure of the final PCR product containing the epitope tagging DNA module with regions identical to chromosome for inducing homologous recombination: T. gondii CAT cassette is flanked on the 5′ side by a 2.4 kb of 3HA tag inserted genomic region of ORF25.m01787 cloned in frame with a 3HAA tag and on the 3′ side by 1.5kb of genomic 3′ flanking region of the ORF25.m01787 target locus. Transfection of the PCR product results in the homologous recombination at the target gene locus and insertion of a C-terminal 3HA epitope sequence in the genome.
E: A schematic view of the altered target gene chromosomal locus with its C-terminal HA tag: The various primers designed and used for verification of the double cross over event in the target gene locus by diagnostic PCR are shown in the figure.