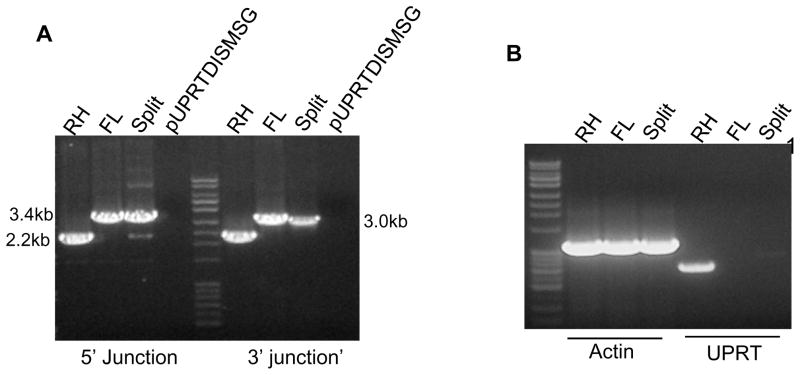
Figure 7. Confirmation of the UPRT gene deletion using split cassette and full length gene deletion strategies.
A: Genomic DNA from wild type RH and drug resistant parasites obtained after transfection using full-length UPRT disruption cassette (FL) and Split deletion cassette (Split) were subjected to PCR analysis using primers DP7, DP9 and DP12 (5′ junction) and primers DP8, DP11 and DP12 (3′ junction). Plasmid pUPRTDISMSG was used as the negative control. This demonstrates the effectiveness of both split and FL constructs in obtaining the UPRT deletion.
B: RT-PCR experiments using cDNA isolated from wild type RH and UPRT deletion clones obtained by either the full-length (FL) or by split cassette (Split) deletion strategy. Primers designed for the T.gondii actin gene resulted in the amplification of a 1.1kb gene transcript from all of the parasites. UPRT gene specific primers amplified a 760bp transcript only from the wild type (RH strain) parasite cDNA and not from either UPRT knock out parasite strains.