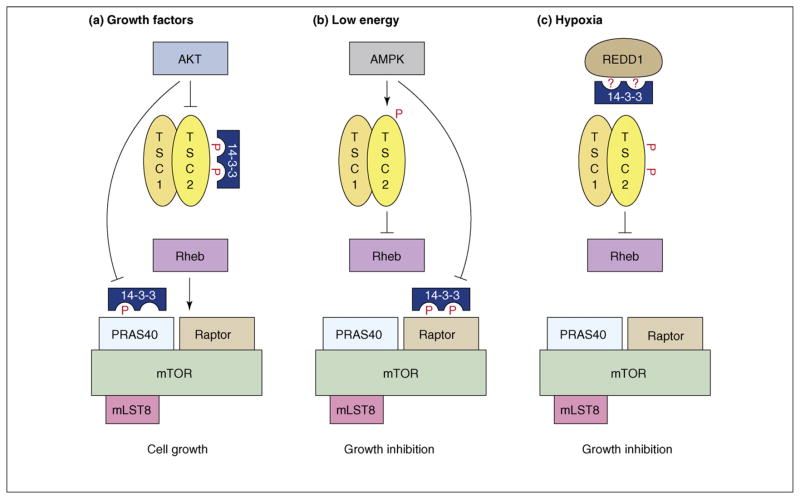
Figure 2.
Functions of 14-3-3 in TORC1 signaling. (a) Under growth conditions, the AKT kinase is activated downstream of the insulin receptor (not depicted) and in turn activates TORC1 by phosphorylating TSC2 and PRAS40 on sites that mediate 14-3-3 binding and that relieve the inhibitory effects of these proteins. (b) AMPK is activated under conditions of low energy and inhibits TORC1 signaling by phosphorylating TSC2 and Raptor, thus, stimulating TSC2 activity and inhibiting Raptor function. AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of Raptor is required for the energy checkpoint induced by AMPK, and the sites that are phosphorylated mediate 14-3-3 binding. (c) REDD1 (DDIT4) expression is induced under hypoxic conditions and REDD1 inhibits TORC1 activity in a TSC2-dependent manner. REDD1 has been reported to reverse the inhibition of TSC2 by promoting the movement of 14-3-3 proteins from TSC2 to REDD1.