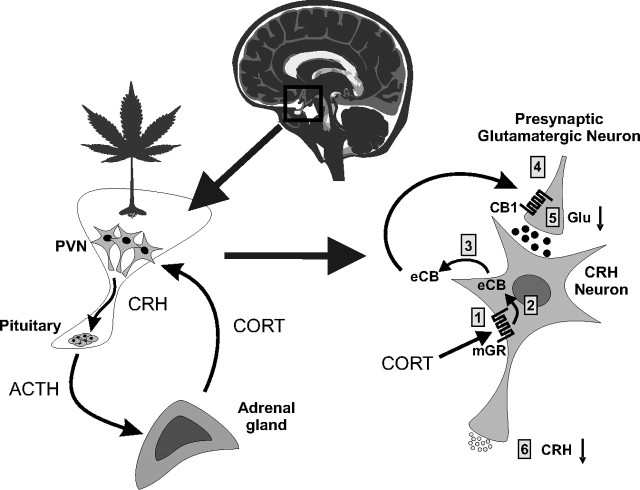
Figure 2.
Fast-feedback inhibition of the HPA axis via glucocorticoid-induced eCB release in the hypothalamus. Left, Stress activation of the HPA axis consists of CRH secretion from PVN neurons and CRH-evoked ACTH secretion from the pituitary, which, in turn, stimulates corticosteroid (CORT) release from the adrenal cortex and CORT feedback onto the PVN. Right, In PVN CRH neurons, CORT binds to a membrane-associated glucocorticoid receptor (mGR) (1), which causes eCB synthesis in CRH neurons (2) and retrograde eCB release (3); eCB binds to presynaptic CB1 receptors on glutamate terminals (4) and inhibits glutamate release (5) onto the CRH neurons, suppressing the excitatory synaptic drive and decreasing CRH neuron activity and CRH release (6), which suppresses HPA axis activation.