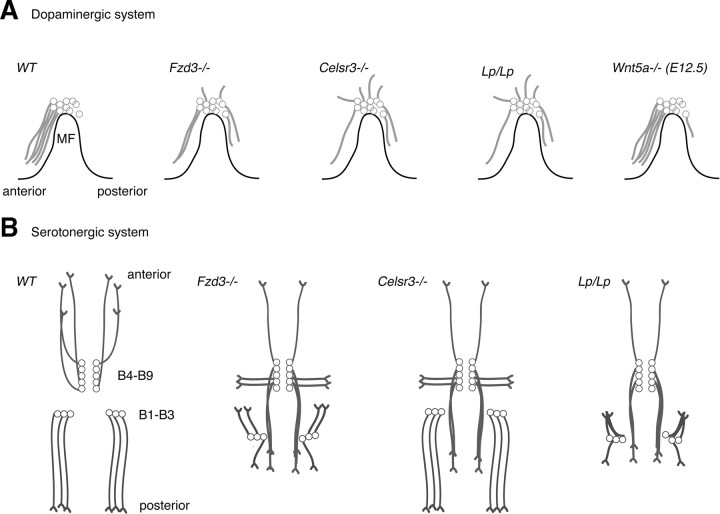
Figure 9.
Axon guidance defects in the brainstem region of PCP and Wnt5a mutant mice. Schematic representation of the embryonic mesodiencephalic dopamine (mdDA) system (A, sagittal view) and ascending and descending serotonergic systems (B, horizontal view). A, In wild-type (WT) mice, mdDA axon projections are oriented anteriorly. Frizzled3, Celsr3, and Vangl2 (Lp/Lp) mutant mice display aberrant dorsal and caudal projections (from E12.5 until E17.5, the latest time point examined). Wnt5a mutant mice display a transient abnormal caudal projection at E12.5. B, In wild-type mice, ascending serotonergic neurons (B9–B4) project their axons anteriorly, whereas descending neurons (B3–B1) give rise to posteriorly directed axon projections. Fzd3 and Vangl2 (Lp/Lp) mutant mice show ascending neurons that project their axons posteriorly or laterally and descending neurons that project axons anteriorly. Celsr3 mutant mice predominantly show defects in ascending axon projections. Descending projections in Vangl2 mice show hyperfasciculation phenotypes not found in Fzd3 or Celsr3 mutant mice.