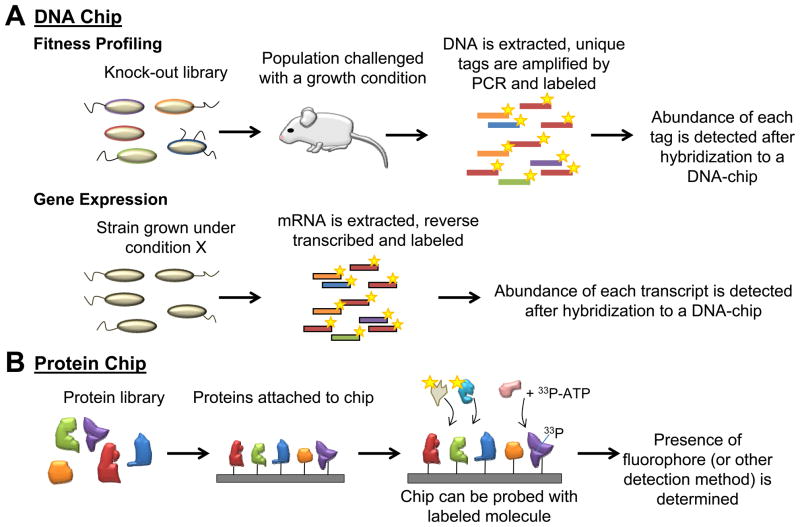
Figure 2.
Microarray technology has enabled HTP studies that can be aimed at the detection of genome-wide interactions. Simultaneous detection of thousands of knock-out strains, gene transcripts, or protein interactions can be performed. Two main types of microarray chips are shown: (a) DNA and (b) protein. (a) DNA oligonucleotides fixed to the chip can hybridize with labelled DNA generated after growth of cells under specific conditions. (b) Proteins fixed to the chip can interact with a labelled molecule (e.g. metabolite, protein, lipid). Targets of protein kinases can also be detected by kinase-directed 33P-labelling and subsequent radioactivity detection.