Figure 4. Molecular biological or pharmacological inhibition of ARNO attenuates glucose-induced activation of Arf6 in INS 832/13 pancreatic β-cells.
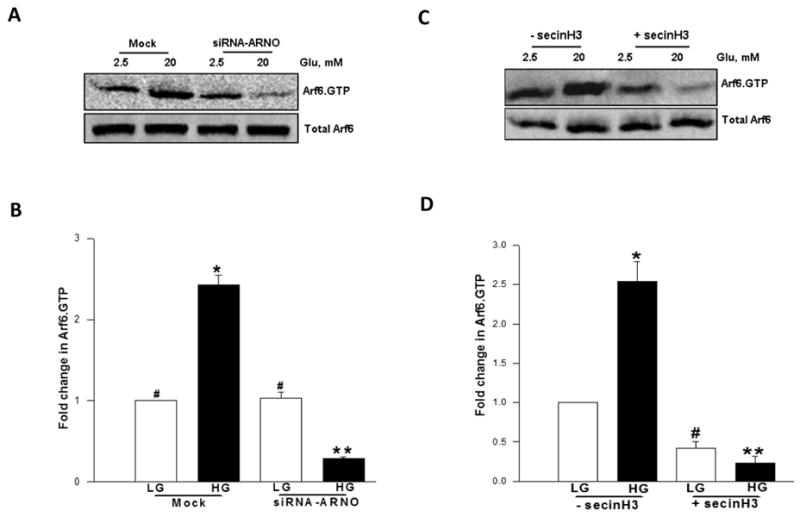
Panel A: INS 832/13 cells were either mock-transfected or transfected with siRNA-ARNO and cultured for 48 h following which cells were stimulated in the presence of either low glucose [LG, 2.5 mM] or high glucose [HG, 20 mM] for 30 min at 37°C. The relative amounts of activated Arf6 [i.e, Arf6.GTP] were determined by pull down assay. Total Arf6 from cell lysates was used as the loading control and a representative blot from three independent experiments is shown.
Panel B: Data shown in the panel A were analyzed densitometrically and expressed as fold change in Arf6.GTP over basal and are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * represents p < 0.05 vs. mock transfected low glucose; **p < 0.05 vs. mock transfected high glucose, and data points with similar symbol do not differ statistically.
Panel C: INS 832/13 cells were incubated overnight in the presence or absence of secinH3 [50 μM] and stimulated with either low glucose [LG, 2.5 mM] or high glucose [HG, 20 mM] in the continuous presence or absence of secinH3 [50 μM] for 30 min. Relative degrees of Arf6 activation was quantitated as described in Panel A. Total Arf6 from cell lysates was used as the loading control and a representative blot from three independent experiments is shown.
Panel D: Data shown in the Panel C are analyzed densitometrically and expressed as fold change in Arf6.GTP over basal. Data are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * and # represents p < 0.05 vs. low glucose without secinH3; and ** p < 0.05 vs. high glucose without secinH3.
