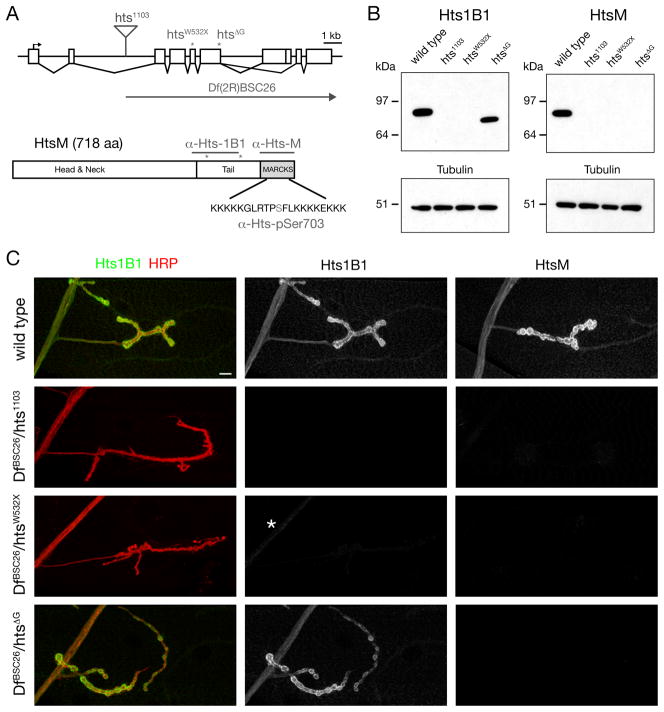
Figure 1. Hts-M is present pre- and postsynaptically at the Drosophila NMJ.
A) Schematic of the Drosophila hts locus. The position of the transposon and EMS-induced mutations are indicated (asterisks). The Hts-M isoform present at the Drosophila NMJ encodes a 718 aa long protein that contains a C-terminal MARCKS domain. Epitopes of the different Hts-M antibodies are indicated.
B) Western Blots of third instar larval brain extracts. Anti-Hts1B1 and anti-Hts-M recognize single protein bands at approximately 80 kDa. The htsΔG mutations results in a truncated protein that can be detected using anti-Hts1B1 but not with anti-Hts-M.
C) Analysis of Hts protein distribution at the Drosophila NMJ using the antibodies Hts-M and Hts1B1. In DfBSC26/hts1103 mutant animals no Hts1B1 or Hts-M staining can be detected. In DfBSC26/htsW532X mutant animals small remnants of protein can be detected by the Hts1B1 antibody in the motoneuron axon (asterisk). In DfBSC26/hts1103mutant animals significant amounts of Hts-M protein can be detected by Hts1B1, however no protein can be detected with the Hts-M antibody.