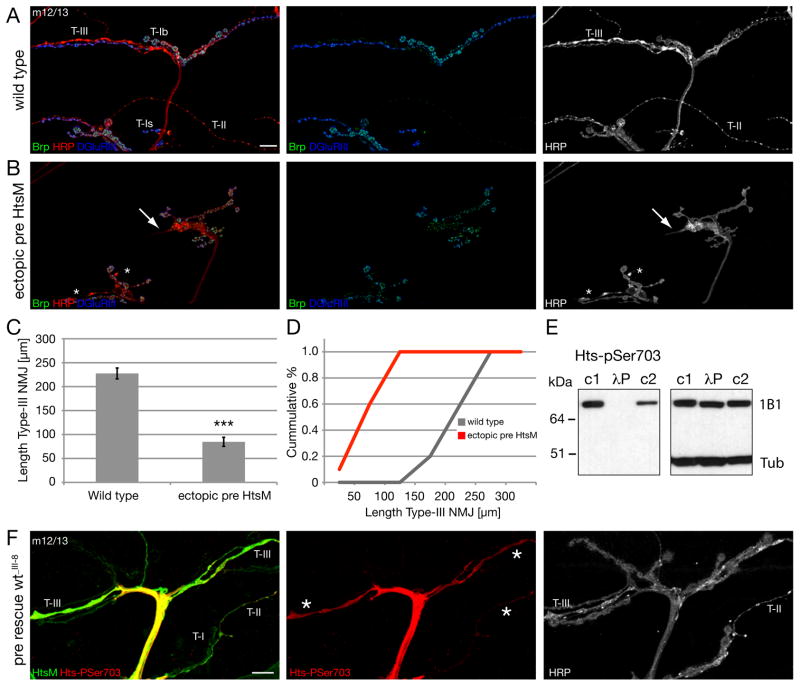
Figure 7. Ectopic expression of Hts-M can restrict synapse formation and growth.
A-C) NMJs on muscles 12/13 stained for the presynaptic active zone protein Brp (green), the presynaptic membrane (HRP, red) and postsynaptic glutamate receptors (DGluRIII).
A) Wild type NMJ. Type II and III synapses cover large areas of muscles 12 and 13.
B) Expression of high levels of Hts-M presynaptically in a wild type background (elavGal4; scaGal4 crossed to 2 copies of UAS-Hts-M). Synapse formation of type II and type III synapses is severely suppressed. The arrows indicate the tip of type III synapses with altered morphology and the asterisks indicate type II synapses.
C, D) Quantification of NMJ length of type III synapses. The ectopic expression of Hts-M reduces the mean total length of type III synapses on muscle 12 from 227 μm to 84 μm (n = 10); p < 0.001 compared to wild type, ANOVA; Error bars represent SEM).
E) The Hts-pSer703 (UPS) antibody recognizes only phosphorylated Hts-M. In untreated larval brain extracts (c1 and c2) anti-Hts-pSer703 detects a protein of identical size as the Hts-1B1 antibody (right blot). The signal is absent in larval brain extracts treated for 5 min with l-phosphatase (lP). c1: identical buffer as in lP treated lane including phosphatase inhibitors; c2: standard Ripa buffer including phosphatase inhibitors. The image on the right is the same Western blot after stripping analyzed with anti-Hts-1B1 and anti-Tubulin antibody.
F) To analyze the distribution and phosphorylation level of presynaptic Hts-M we stained hts mutant animals that expressed Hts-M only presynaptically (elavGal4; DfBSC26/hts1103; UAS hts-wt_III-8/+). In these animals all phenotypes associated with hts mutations are rescued. We analyzed the distribution of the Hts-M and phospho-Hts at muscles 12/13 where we can simultaneously analyze type I, II and III synapses as stated in A. While we detect no or only very low levels of phosphorylated Hts-M in type I boutons we observe high levels of phosphorylated Hts-M in both type II and type III synapses. Scale bar in A corresponds to A, B, F 10 μm.