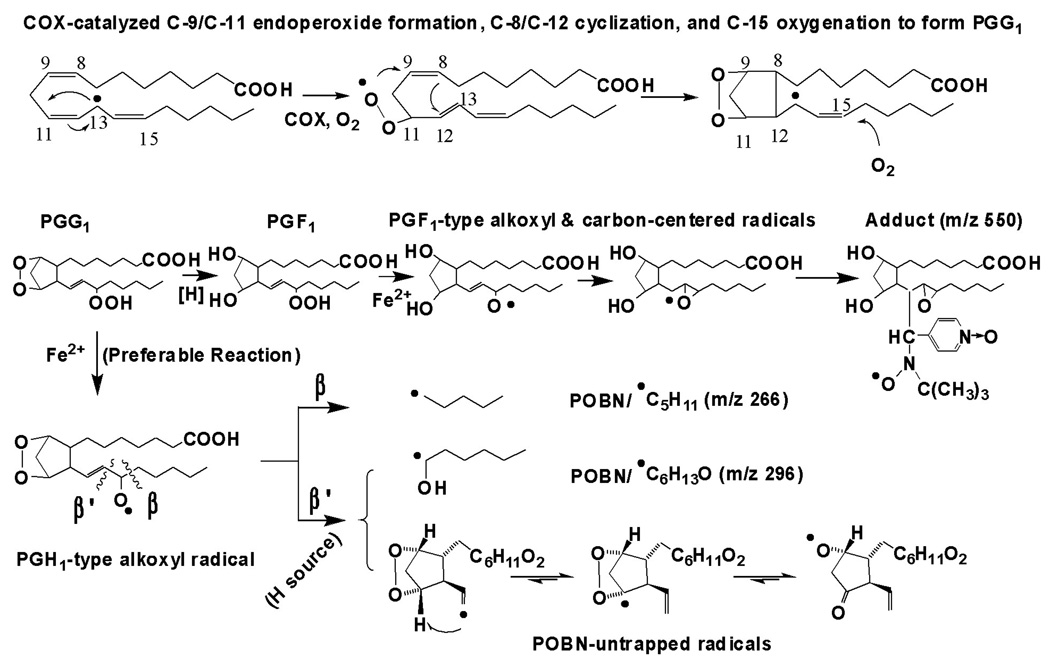
Scheme 1.
Proposed mechanism of COX-DGLA peroxidation to form DGLA-derived free radicals via C-15 oxygenation, a peroxidation pathway similar to COX-AA [17].
Note that in both COX-AA and DGLA peroxidation, free radial reactions including formation of C-13 radicals, C-9/C-11 endoperoxide bridge (addition of the first O2), C-8 and C-12 cyclization, and C-15 oxygenation (via peroxidase activity of COX, addition of the second O2). The source of H needed for the β’-scission in this pathway could be hydrophilic COX channel residues Tyr-385, Tyr-348, and Ser-530, as well as H2O [29–30]. The proposed oxygen-centered radicals can be further decomposed to the other products, e.g. C-9 to C-11 elimination to form malonaldehyde.