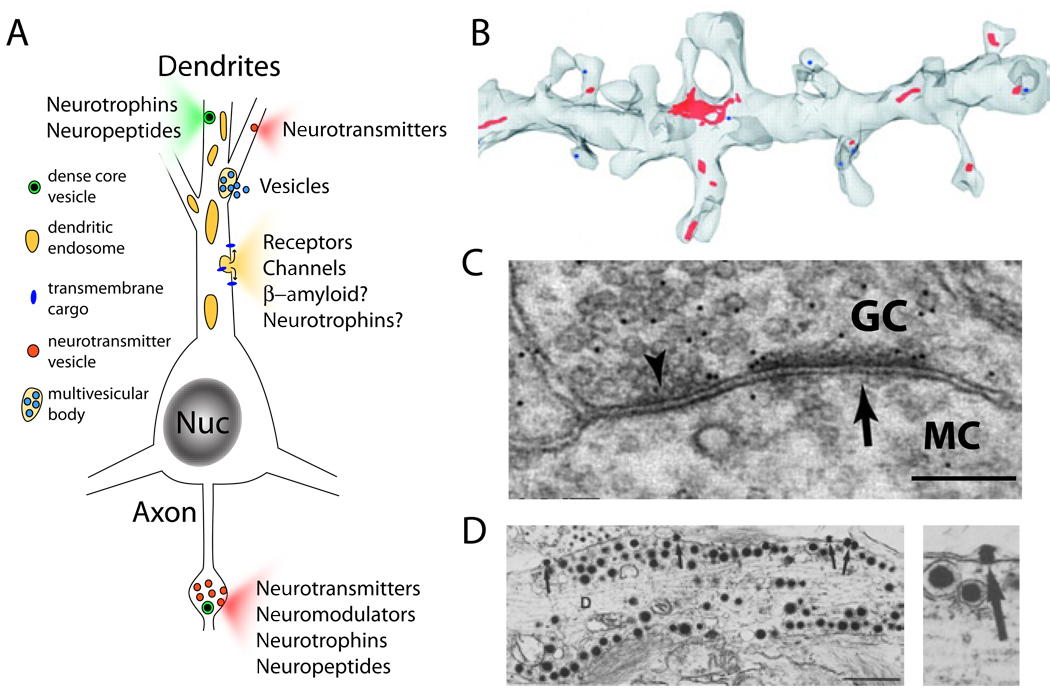
Figure 1. Dendritic Organelles for Exocytosis.
(A) Schematic of a neuron showing exocytosis from dendrites and axons. Dendritic secretory cargo includes soluble factors such as neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, and neurotrophins as well as transmembrane proteins including neurotransmitter receptors and ion channels.
(B) Serial section reconstruction of electron micrographs from hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons showing recycling endosomes in red. Note the presence of recycling endosomes in several of the dendritic spines. Reprinted with permission from Cooney et al. (2002).
(C) Electron micrograph of a dendrodendritic synapse between a granule cell (GC) and a mitral cell (MC) in the olfactory bulb. The inhibitory synaptic specialization is labeled with an arrowhead while the excitatory specialization is labeled with an arrow. Scale bar, 200 nm. Reprinted with permission from Lagier et al (2007).
(D) Dense core vesicles from presumptive vasopressin/oxytocinergic magnocellular neurons in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus. Note the presence of docked dense core vesicles at the dendritic plasma membrane and the presence of vesicle contents in the extracellular space (arrow, right panel). Scale bar, 1 µm. Reprinted with permission from from Pow and Morris (1989).