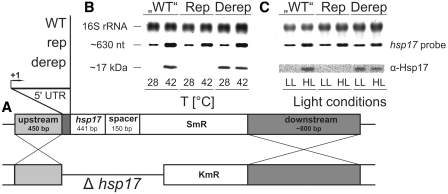
Figure 6.
Effect of chromosomally integrated hsp17 UTR variants on Hsp17 production in Synechocystis. (A) Outline of the strategy for construction of hsp17 mutants. The Synechocystis HK-1 (Δhsp17) strain was used for integration of hsp17 and its 5′-UTR via up and downstream flanking sequences. SmR, spectinomycin resistance; KmR, kanamycin resistance. Homologous recombination resulted in generation of the so-called ‘WT’, Rep and Derep strains. (B and C) Determination of hsp17 mRNA and Hsp17 protein levels by northern and western analysis, respectively. Total RNA and protein was extracted from Synechocystis cells incubated at either 28 or 42°C. Ethidium bromide stained 16 s rRNA served as a loading control in northern blot experiments. Equal amounts of total protein were checked by Coomassie-stained SDS–PAGE gels (data not shown). A digoxygenin-labeled RNA probe was used to detect hsp17 transcripts, Hsp17 protein was detected via monoclonal α-Hsp17 antibody. (C) Synechocystis cells were incubated under low light (LL: 30 µmol photons m−2 s−1) or high light (HL: 600 µmol photons m−2 s−1) conditions at 28°C for 30 min. Temperature-stability of the culture was monitored. Subsequent northern and western analysis was conducted as described above.