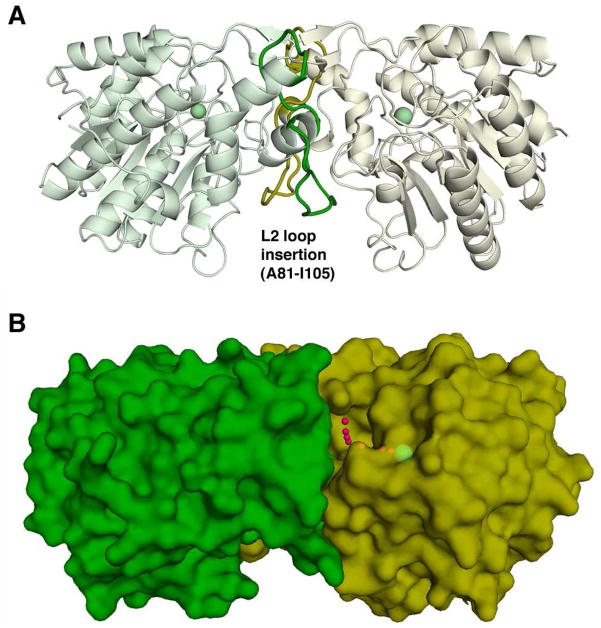
Figure 4.
View of the isologous APAH dimer. (A) The L2 loop follows β-strand 2; residues A81-I105 (colored green and yellow in their respective monomers) make extensive hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions with the adjacent protomer that stabilize the APAH dimer. For reference, the active site Zn2+ ion is shown as a green sphere. (B) Small red spheres trace the “L”-shaped path from the dimer surface to the catalytic Zn2+ ion (green sphere).