Fig. 4. T-cell-independent and T-cell-dependent mechanisms of autoantibody production.
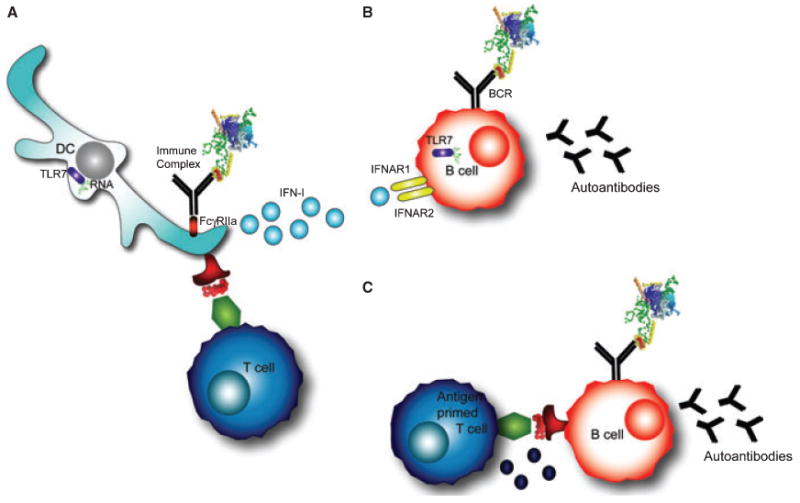
(A) Dendritic cells internalize immune complexes through FcγRIIα. RNA contained in the immune complex stimulates TLR7, resulting in type-I interferon production (IFN-I). In addition, DCs present peptides from the processed antigen complex on their surface to T cells. (B) T-cell-independent B-cell activation occurs in B cells that are stimulated through the B-cell receptor (BCR) and TLR7 by RNA-containing antigens. In addition, interferons signal through IFNAR receptors on the B-cell surface. These signals can induce autoantibody production against the RNA-containing protein complex in some models. (C) T-cell-dependent B-cell activation occurs through the typical T-B cognate interaction that provides T-cell help and leads to autoantibody production.
