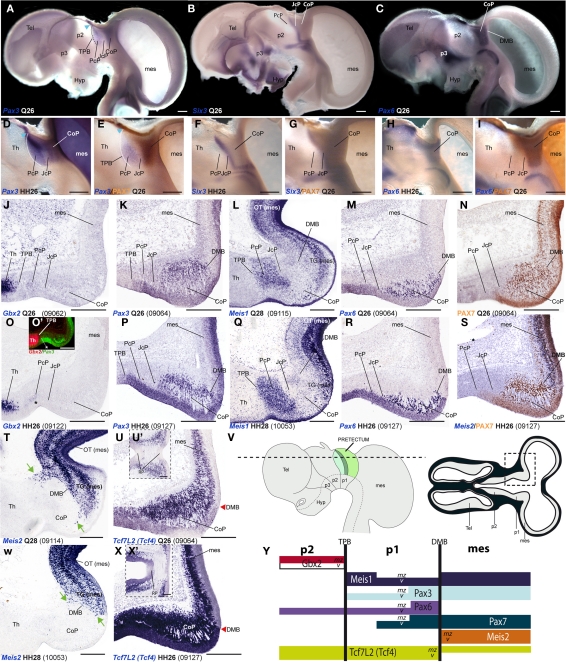
Figure 2.
Pairwise comparison of gene patterns in the developing pretectum of Q26 quail or HH26 chicken embryos (as identified at left bottom corner of each panel). The markers shown are Pax3 (A,D,E,K,P), Six3 (B,F,G), Pax6 (C,H,I,M,R), PAX7 (E,I,N,S), Gbx2 (J,O,O′), Meis1 (L,Q), Meis2 (S,T,W), and Tcf7l2 (U,U′,X,X′). (A–I) Whole-mount in situ hybridization and immunoreaction processed material identify the main pretectal boundaries and define an anteroposterior tripartition. Blue arrowhead in (A,D,E): Pax3 expression extends continuously from the pretectum into the thalamic habenular region. (J–X) Horizontal sections at corresponding levels in both species illustrating distribution along the radial dimension of the studied markers. The pairwise comparable panels are organized one on top of the other (J,O,K,P, …). The numbers between brackets at the bottom of each panel give the code identifying the specimen in our collection (data from the same specimen may appear in different panels or plates). Inset (O′) compares in pseudocolor the patterns of Gbx2 and Pax3, demonstrating that the cell group marked with an asterisk (O,O′) lies caudal to the thalamo-pretectal boundary. Insets (U′,X′) show horizontal sections passing through the roof of the pretectum, where Tcf7l2 is not expressed. Green arrows in (T,W): Meis2 positive cells at the CoP. The schemata in (V) represent a lateral view of the brain indicating the horizontal section plane used, and the position in such sections of the pretectal region that appears magnified in the panels (dashed box). (Y) Schema of gene combinations mapped in the midbrain (mes) and diencephalic prosomeres p1 and p2. Each gene is represented by a color-coded bar. The upper and lower halves of each bar represent gene expression in the mantle (mz) or ventricular zones (v) respectively. Scale bars = 300 μm.