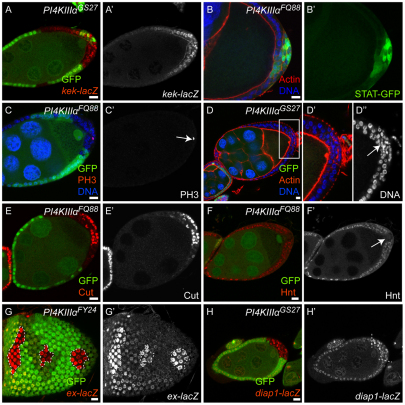
Fig. 2.
Effects of PI4KIIIalpha mutations on different signaling pathways. Mutant cells are marked by the absence of GFP (green), except in B where we generated unmarked clones in order to visualize the 10×STAT-GFP reporter and PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells were identified by the loss of their monolayered epithelial structure outlined by actin staining. (A,A′) A Drosophila egg chamber containing PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs, expressing the EGFR signaling reporter kekkon-lacZ and stained for β-gal (red in A, gray in A′). (B,B′) An egg chamber containing PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs, expressing the JAK/STAT signaling reporter 10×STAT-GFP (green). Both EGFR and JAK/STAT signaling pathways were correctly activated and transduced in the PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs, as indicated by the normal levels of β-gal staining (A,A′) and GFP signal (B,B′). (C-F′) Egg chambers containing PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs stained for phosphorylated Histone H3 (PH3, red, C), Actin (red, D), DNA (blue, C,D), Cut (red, E) and Hnt (red, F); the PH3, Cut and Hnt channels are also shown separately (C′,E′,F′); the boxed region in D is shown at higher magnification in D′ and D″ (DNA channel only). PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs remained in the mitotic cycle after stage 6, as indicated by the presence of PH3-positive cells (C′, arrow) and multilayered cells with smaller nuclei (D″, arrow). PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs failed to downregulate Cut (E) and to upregulate Hnt (F) after stage 6. These results indicate that Notch signaling is compromised in PI4KIIIalpha mutant PFCs. (D,E) Note that PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells at the lateral side of the egg chambers show normal epithelial structure (D) and correctly downregulated Cut expression (E), as in the wild-type cells. (G-H′) Egg chambers containing PI4KIIIalpha mutant FCs, expressing the Hippo signaling reporters ex-lacZ (G) and diap1-lacZ (H), stained for β-gal (red in G,H; gray in G′,H′). Upregulation of both reporters indicates that Hippo signaling is disrupted in PI4KIIIalpha mutant FCs. Scale bars: 10 μm.