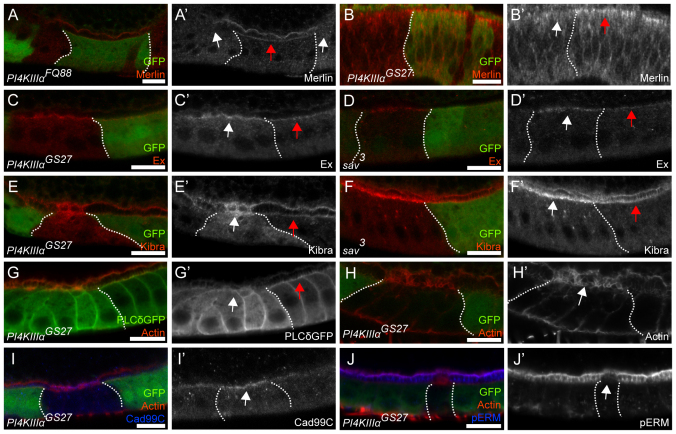
Fig. 3.
Merlin mislocalization from the apical membrane in PI4KIIIalpha mutant follicle cells and eye disc cells. Clone boundaries are marked by dotted white lines. Mutant cells are marked by the absence of GFP (green), except in G where we generated unmarked clones in order to visualize the Ubi-PH-PLCδ-GFP reporter. PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells were identified by the abnormal actin structure on the apical domain. FCs and eye disc cells are orientated with the apical side up. (A-B′) The follicular epithelium (A) and the imaginal eye disc epithelium (B) containing PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells stained for Merlin (red in A,B; gray in A′,B′). (C-F′) Egg chambers containing PI4KIIIalpha (C,E) or sav (D,F) mutant FCs stained for Expanded (red in C,D; gray in C′,D′) and Kibra (red in E,F; gray in E′,F′). Merlin, Expanded and Kibra localization in wild-type cells is indicated with red arrows. Merlin disappears from the apical and junctional region of the mutant cells (A′,B′, white arrow), whereas Expanded (C′, white arrow) and Kibra (E′, white arrow) are upregulated but remain localized. Upregulation of Expanded (D′, white arrow) and Kibra (F′, white arrow) is similarly observed in sav mutant FCs. (G-J′) Egg chambers containing PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells, expressing the PI(4,5)P2 reporter Ubi-PH-PLCδ-GFP (G), stained for GFP (green in G; gray in G′), actin (red in G-J; gray in H′), Cad99C (blue in I; gray in I′) and phospho-ERM proteins (blue in J; gray in J′). The PI(4,5)P2 reporter is absent from the apical membrane of the mutant cells (G′, white arrow), in contrast to the wild-type cells (G′, red arrow). PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells exhibit abnormal actin spikes on the apical side (H′, white arrow) as marked by the microvillus marker Cad99C (I′, white arrow). The apical microvilli region of PI4KIIIalpha mutant cells shows depletion of phospho-ERM proteins (J′, white arrow). Scale bars: 10 μm.