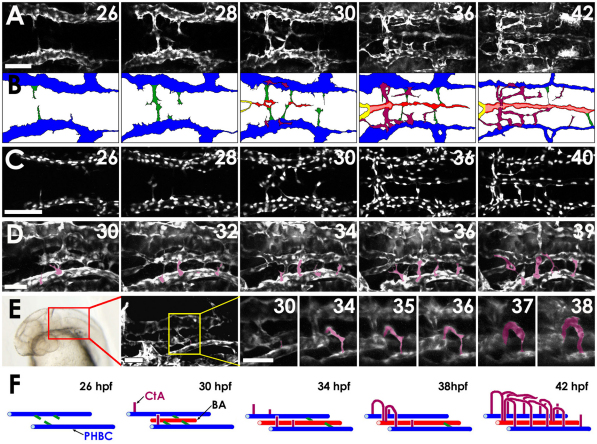
Fig. 2.
Two-photon time-lapse imaging of the assembling hindbrain vasculature. (A) Dorsal time-lapse images of BA and CtA formation in the hindbrain of a 26-42 hpf Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 zebrafish embryo (see Movie 1 in the supplementary material). (B) Diagrams of the vessels in A, showing PHBCs (blue), medial sprouts from the PHBCs giving rise to and temporarily connecting to the BA (green), the assembling BA (red), and CtAs sprouting dorsally from the PHBC to form a network connecting to the BA (purple). (C) Dorsal time-lapse images of BA formation in the hindbrain of a 26-40 hpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP)y7 embryo (see Movie 2 in the supplementary material). (D) Dorsal-lateral time-lapse images of CtAs sprouting dorsally from the PHBCs in the hindbrain of a 30-39 hpf Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 embryo (see Movie 3 in the supplementary material). CtAs emerging from the left PHBC are pseudocolored purple for ease of visualization. (E) Frontal dorsal-lateral time-lapse images of the r3 CtA (pseudocolored purple for ease of visualization) sprouting dorsally from the PHBCs in the hindbrain of a 30-38 hpf Tg(kdrl:GFP) embryo (see Movie 4 in the supplementary material). The red box on the transmitted light image indicates the area visualized in the adjacent confocal image, and the yellow box in that image indicates the area shown at higher magnification in the remaining panels, which includes the r3 CtA. (F) Model of hindbrain vascular development (color scheme as in B). Scale bars: 50 μm in A,C; 25 μm in D,E.