Fig. 5.
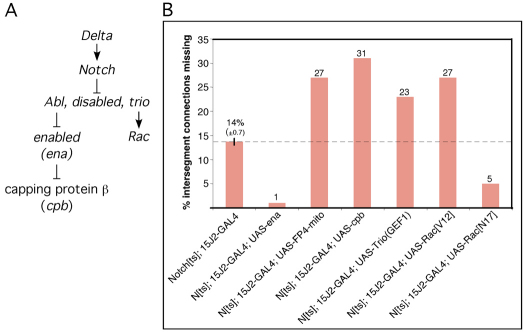
Notch interactions with Abl pathway in longitudinal pioneers. (A) Model for the Notch/Abl signaling module. Schematic representation of the non-canonical Notch/Abl signaling pathway. Arrows indicate positive regulation; ⊥ indicates negative regulation. In response to ligand, Notch antagonizes the activity of the Abl signaling module, which includes Abl tyrosine kinase, the adaptor protein Disabled, and Trio, a guanine exchange factor (GEF) for Rho GTPases. Abl, in turn, is a negative regulator of Enabled, a protein that inhibits capping of actin filaments, whereas Trio is a positive regulator of Rac GTPase. (B) Genetic interactions of Abl pathway components with Notch in dMP2 and vMP2. Embryos were prepared and early longitudinal connections quantified. Bars indicate percentage of intersegment connections missing. All genotypes shown were significantly different from Notchts (P<0.01; ANOVA). None of the Abl pathway reagents produced a dominant phenotype in a wild-type background by this assay (<2% of intersegment connections missing). The thin vertical line on the Notchts; 15J2-GAL4 bar shows s.e.m.