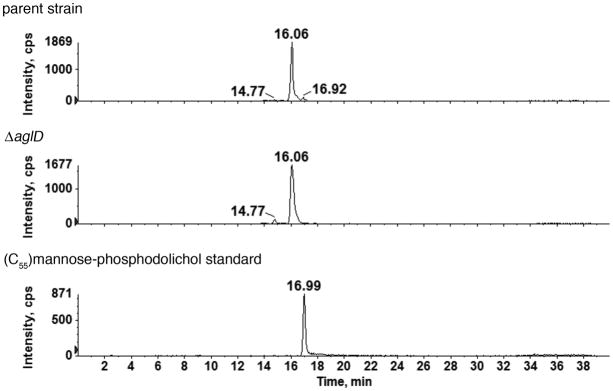
Fig 4.
The absence of AglD eliminates mannose-modified phosphodolichol. Normal phase LC extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of the dolichylphosphate-hexose [M-H]− ion at m/z 1079.8 from the parent strain (upper panel) and the ΔaglD (middle panel) are shown. The peaks at different retention times reflect the existence of three different dolichylphosphate-hexose species (Kaminski et al., 2010). The 16.92 min peak is eliminated in the mutant, as compared with the parent strain, suggesting AglD to be specific for the formation of the third monosaccharide-modified phosphodolichol species. The monosaccharide-modified phosphodolichol peak affected by the absence of AglD is retained at the position of a mannose-modified phosphodolichol standard (16.99 min; lower panel). The identities of the two other monosaccharide-modified phosphodolichols with retention times of 14.77 and 16.06 min, respectively, remain to be determined. While the results shown address C55 dolichol phosphate, similar results were obtained with C60 dolichol phosphate (not shown).