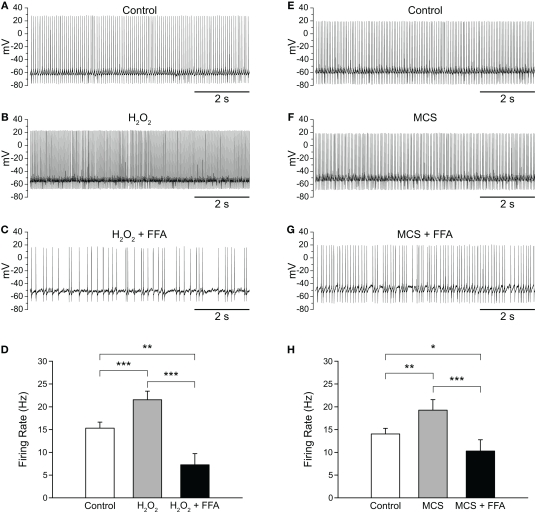
Figure 5.
Flufenamic acid (FFA) reverses H2O2-induced increases in firing rate. (A) Spontaneous activity of a SNr GABAergic neuron under control conditions, (B) following H2O2 (1.5 mM) application, and (C) with FFA (20 μM) applied in the continued presence of H2O2. (D) The H2O2-induced increase in firing rate was reversed by FFA and the resulting firing rate suppressed below control. (E) Activity of another SNr GABAergic neuron under control conditions, (F) following amplification of endogenous H2O2 with MCS (1 mM), and (G) in FFA (20 μM) in the continued presence of MCS. (H) Increases in firing rate induced by amplified endogenous H2O2 were similarly reversed and suppressed below control levels by FFA. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).