FIGURE 1.
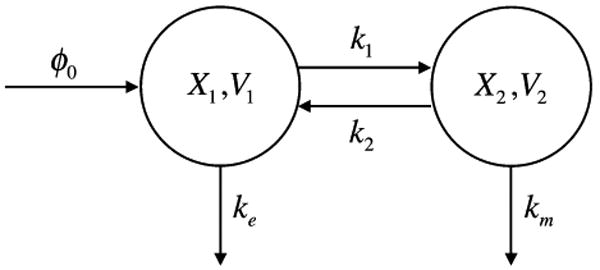
Two-compartment pharmacokinetic model. A drug is infused into the blood stream at a constant rate ϕ0. The drug has concentration X1 in compartment 1, which represents the blood with volume V1, is excreted by a first-order process with rate constant ke, and is transported to compartment 2 with a rate constant k1. The drug has concentration X2 in compartment 2, which represents the target organ with volume V2, is metabolized by a first-order process with rate constant km, and is transported to compartment 1 with a rate constant k2. The relative sizes of the compartments is given by ρ = V2/V1.
