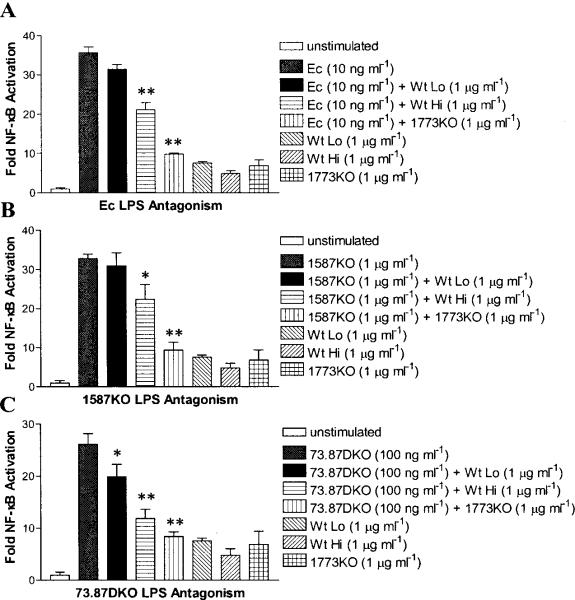
Fig. 4.
Hemin-dependent control of lipid A phosphatase modulates the ability of P. gingivalis LPS to suppress host TLR4 activation. HEK293 cells expressing human TLR4 and MD-2 and harboring a NF-κB-luciferase reporter were exposed to the indicated doses of LPS for 4 hours, and TLR4-dependent NF-κB activation was determined by Fire-fly luciferase assay. The relative abilities of Wt Lo LPS, Wt Hi LPS, and 1773KO LPS to antagonize (A) Ec LPS-dependent, (B) 1587KO LPS-dependent, or (C) 73.87DKO LPS-dependent activation of TLR4. The results shown are means ±SD of triplicate samples from one of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences (* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; two-tailed unpaired t tests) for the level of TLR4 activation achieved for LPS agonist alone vs. the level achieved for LPS agonist combined with either Wt Hi LPS or 1773KO LPS.