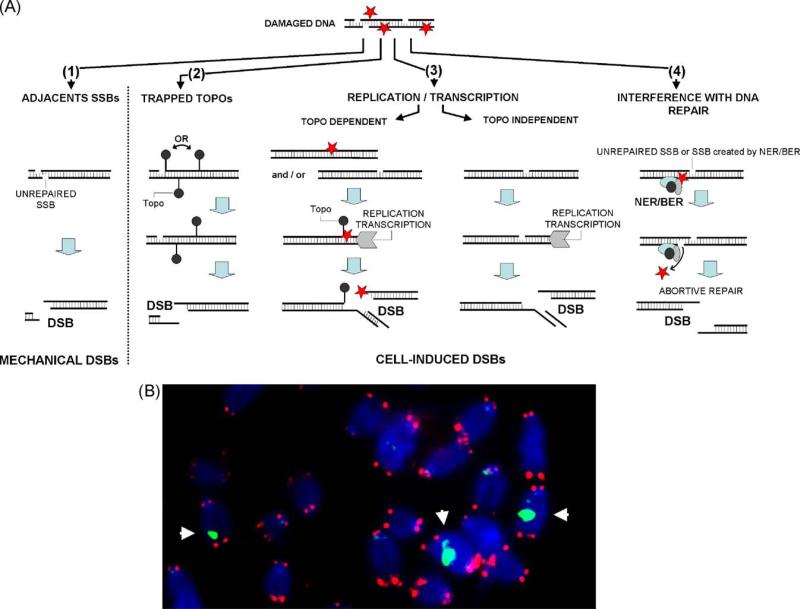
Fig. 2.
Oxidative stress can lead to DNA DSB formation. (A) A DSB can arise when two SSBs form close to each other (1), when topos cleave next to a SSB (2) and when ROS-induced DNA damage interferes with both DNA replication and transcription (3). A DSB is generated during DNA repair when excision of a modified base takes place near an unrepaired SSB. Oxidative DNA lesions can also interfere with reversible topo cleavage complexes during DNA replication and RNA transcription. In such cases, DNA/RNA polymerase forks run off the DNA to generate DSBs. Finally, DSBs can also appear when transcription and replication forks collide directly with SSBs or other ROS-induced lesions. Rarely, interference during DNA repair by BER also leads to DSB formation (4). (B) Representative image showing DNA DSBs induced by oxidative stress on mouse chromosomes. Blue: DNA; red: FISH signal indicating telomeres; green: DSBs visualized by γ-H2AX foci. White arrows indicate chromosomes containing a DSB.