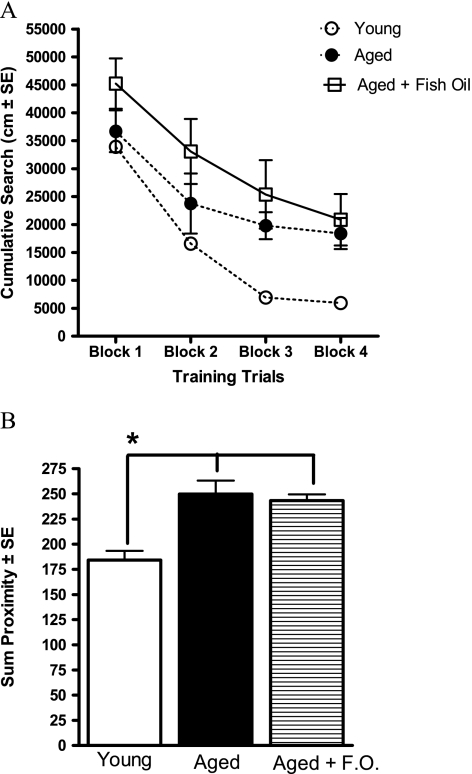
Figure 5.
(A) The cumulative search during the acquisition of a spatial learning task in the water maze. Each block represents the average of five training trials. Young rats were more proficient in learning the location of the escape platform compared with both the aged control and the aged + fish oil (FO) groups. (B) Proximity to escape platform location during probe trials. Data are the sum of proximity to the escape platform location during probe trials 2–4. Young rats perform significantly better than the aged control and aged + FO groups, and there are no differences between the two aged groups. *p < .05.