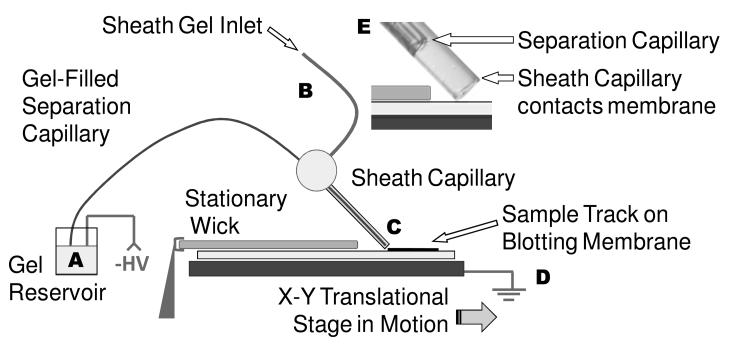
Figure 1.
Instrument overview. Sample is injected at the inlet of the separation capillary (A). The protein mixture migrates the gel-filled capillary under an electric field that is generated by the application of negative high voltage (A) and ground (D). Proteins exit the capillary as it drags over the surface, and deposit on the blotting membrane (C). A translational stage moves the blot past the end of capillary to preserve the protein separation on the membrane. Gel pumped through a sheath capillary (B) that surrounds the latter portion of the separation capillary and and makes direct contact with the blotting membrane (E). The blotting membrane (and wick overlay) are moistened with 50:50 (v:v) methanol: electrophoresis buffer.