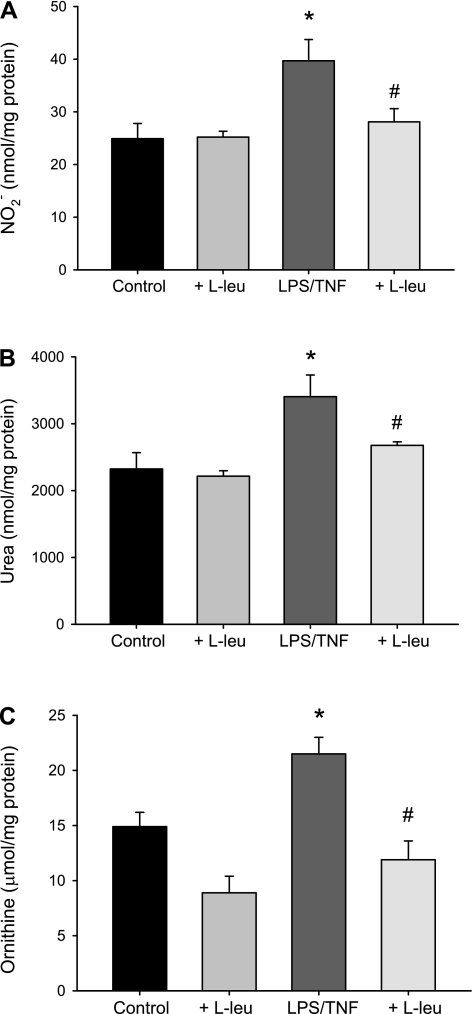
Fig. 3.
Inhibiting l-arginine uptake prevented the LPS/TNF-induced increases in nitric oxide, urea, and ornithine production in bPAEC. bPAEC were treated with vehicle or LPS/TNF, and either no added l-leucine (l-leu) or 10 mM l-leu for 24 h, and the media was collected. A: LPS/TNF treatment resulted in significantly greater nitrite (NO2−) production than in the vehicle-treated control bPAEC, and the addition of l-leu prevented the LPS/TNF-increase in NO2− production. Treatment of vehicle control bPAEC with l-leu had little effect on NO2−. B: LPS/TNF treatment resulted in significantly greater urea production than in the vehicle-treated control bPAEC, and the addition of l-leu prevented the LPS/TNF-increase in urea production. Treatment of vehicle control bPAEC with l-leu had little effect on urea production. C: LPS/TNF treatment resulted in significantly greater ornithine production than in the vehicle-treated control bPAEC, and the addition of l-leu prevented the LPS/TNF increase in ornithine production. Values are means ± SE; n = 5–10 in each group. *LPS/TNF different from control, P < 0.01. #LPS/TNF + l-leu different from LPS/TNF alone, P < 0.05.