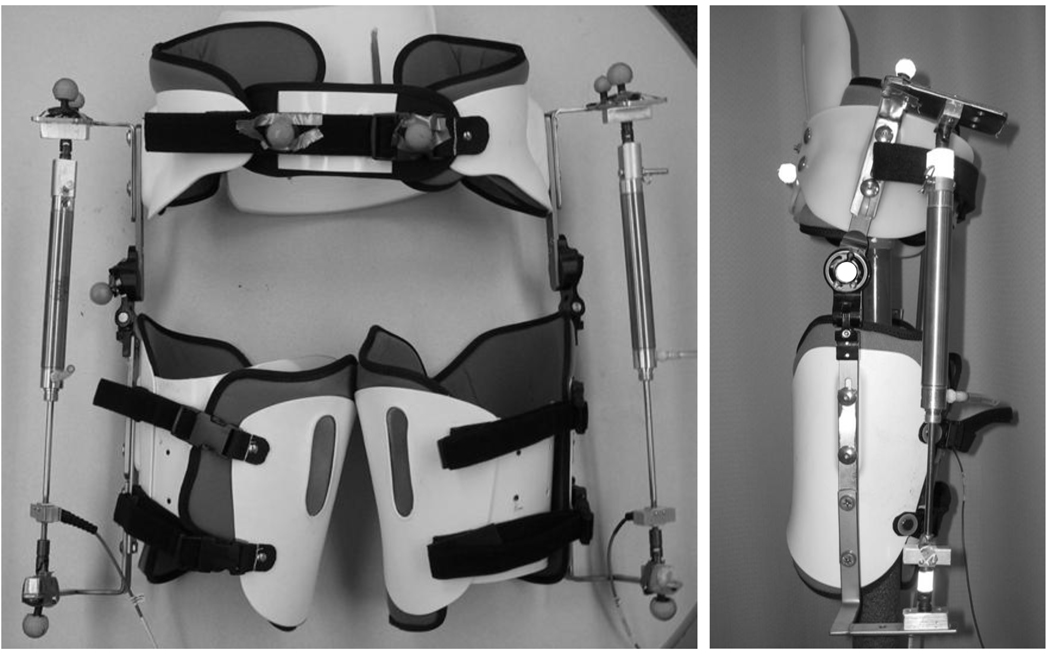
Figure 1.
The bilateral pneumatically powered hip exoskeleton: front (left) and side (right) views. The adjustable exoskeleton consists of a bivalve thigh cuff and a pelvic band, with an added polypropylene lumbosacral support. The thigh and pelvis sections are connected with a joint which allows both flexion and extension, and abduction and adduction. Steel brackets were added for the attachment of the pneumatic cylinder.