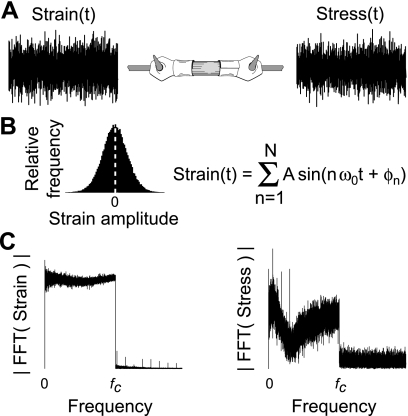
Fig. 2.
A: system analysis similar to the description in Fig. 1 can be applied to muscle fibers using a white noise stimulus. B: the strain signal represents band-limited Gaussian white noise, constructed by summing a series of sine waves of the same amplitude but of random phase, and covering a frequency range up to a prescribed cutoff frequency (fc). Theoretically, this creates a strain signal with a Gaussian amplitude distribution and a flat power spectrum. See materials and methods for further detail. C: representative Fourier transforms of the measured strain stimulus and stress response illustrate the measured behavior from a demembranated fruit fly dorsolongitudinal muscle fiber. FFT, fast Fourier transform; ω0, angular frequency; ϕn, random phase.