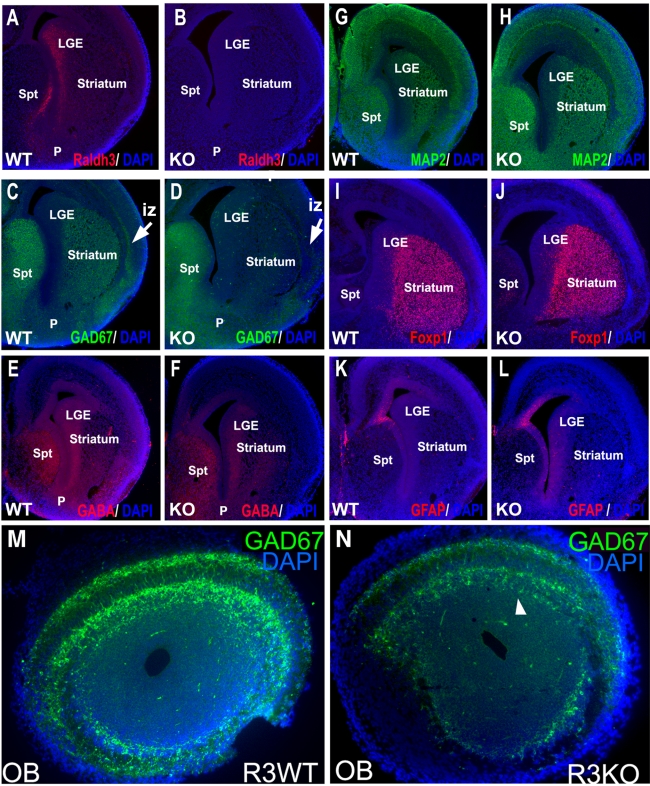
Figure 5. RA is required for GABAergic differentiation of striatal projection neurons and interneurons migrating to the cortex and olfactory bulb.
Immunofluorescence was performed on E18.5 forebrain coronal sections of wild-type (WT) and Raldh3−/− (KO) embryos. (A–B) Raldh3 immunoreactivity in the subventricular zone of the LGE and septum is lost in the mutant. (C–F) In Raldh3−/− embryos, detection of both Gad67 and GABA is greatly reduced in the LGE, striatum, and cortex (note arrows for Gad67); septum is unaffected. (G–L) Loss of Raldh3 does not affect detection of neuronal marker MAP2, striatal projection marker Foxp1, or astrocytic marker GFAP. (M–N) Raldh3−/− embryos exhibit a reduction of Gad67-positive neurons migrating from the LGE to the olfactory bulb when compared to wild-type. All mutants analyzed generated similar results (n = 3). iz, intermediate zone; LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; OB, olfactory bulb; P, pallidum; Spt, septum.