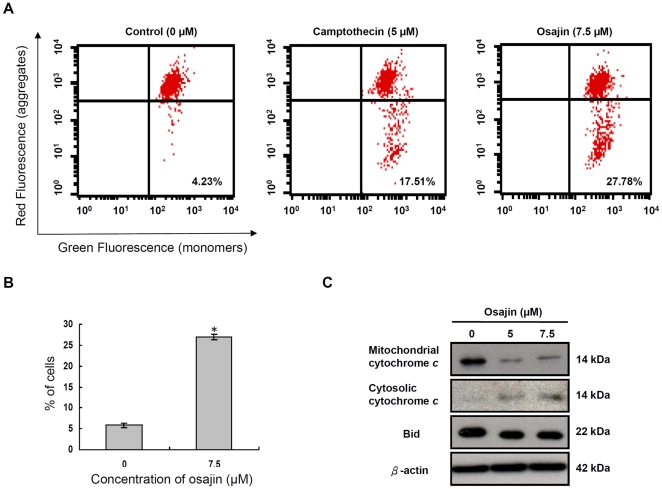
Figure 4. Osajin causes disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and release of cytochrome c into the cytosol.
(A) TW04 cells were treated with 7.5 µM osajin for 24 h before staining with MitoCapture™, a cationic dye. The mitochondrial membrane potential was measured by flow cytometry. The shift-down of fluorescence from red to green indicates the collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential. Camptothecin was used as a positive control for the disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. The percentage of cells with disrupted mitochondrial membrane potential is indicated. (B) The data indicate the percentage of cells with disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. Results are shown as means ± SE of four independent experiments (*P<0.05 versus 0 µM control). (C) Proteins prepared from cells treated with 5 µM or 7.5 µM osajin for 24 h were subjected to Western blot for measurement of Bid and cytochrome c in the cytosol. β-actin was used as internal control to ensure that equal amounts of proteins were loaded in each lane.