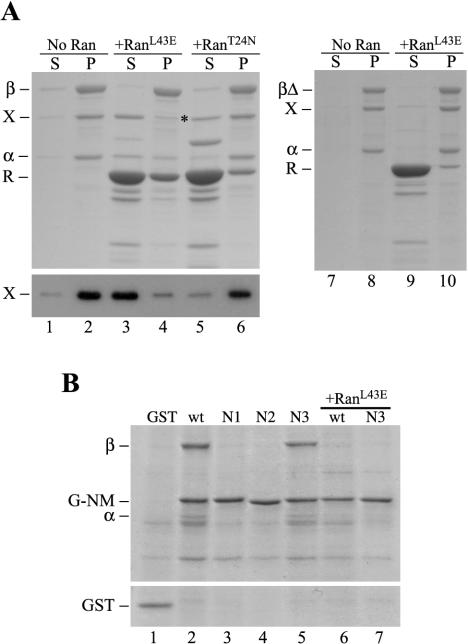
Figure 2.
XCTK2 binding to importin α/β is regulated by the nucleotide state of Ran and is dependent on the Ran-binding domain of importin β. Coomassie-stained gels and anti-CTP1 immunoblot of the supernatants and pellets of S-importin β and S-importin βΔ (βΔ) bind and release assays in the presence and absence of Ran (R). (A) S-importin β bind and release assay with importin α-His and XCTK2 in the absence (No Ran, lanes 1 and 2) and presence of GST-RanL43E-GTP (RanL43E, lanes 3 and 4) or GST-RanT24N-GDP (RanT24N, lanes 5 and 6). The asterisk indicates a contaminating, comigrating band from the RanT24N purification. Bottom, an immunoblot of the same fractions probed with the anti-CTP1 antibody. Right, S-importin βΔ bind and release assay with importin α and XCTK2 in the absence (lanes 7 and 8) and presence of GST-RanL43E-GTP (lanes 9 and 10). (B) Anti-GST immunoprecipitation of GST (lane 1), G-NM (wt, lane 2), NLS-1 (N1, lane 3), NLS-2 (N2, lane 4), and NLS-3 (N3, lane 5). G-NM (lane 6) and NLS-3 mutant (lane 7) anti-GST immunoprecipitations in the presence of His-RanL43E (+RanL43E).