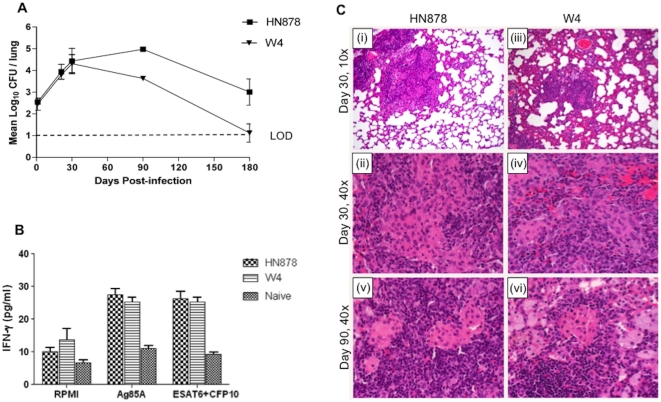
Figure 2. Response to infection of Wistar rats with two closely related Beijing Mtb strains.
A, Pulmonary bacillary load in Wistar rats infected with HN878 or W4. Values are means ± SDs. The difference in Mtb load between both strains at day 90 (P = 0.001) and 180 (P = 0.019) was significant. B, Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) production by lung cells from Mtb infected rats following ex vivo stimulation with ESAT6+CFP10 or Ag85A antigens at day 30 post infection. Values are means ± SE. C, Histopathologic micrographs of lungs of rats infected with M. tuberculosis HN878 versus W4. (i) Infection with strain HN878, 30 days post infection, H&E, magnification 10×. Small, well organized granulomas, demarcated from the rest of the parenchyma. (ii) Same as (i) at magnification 40×. Distinct area rich in macrophages, surrounded by lymphocytes. (iii) Infection with strain W4, 30 days post infection, H&E, magnification 10×. Increased alveolar cell wall thickening is seen. (iv) Same as (iii) at magnification 40×. Granulomas consist of macrophages and lymphocytes. (v) Infection with HN878, 90 days post infection, H&E, magnification 40×. Well organized granulomas with areas rich in macrophages surrounded by large numbers of lymphocytes. (vi) Infection with W4, 90 days post infection, H&E, magnification 40×. Well organized granulomas with a higher number of foamy macrophages.