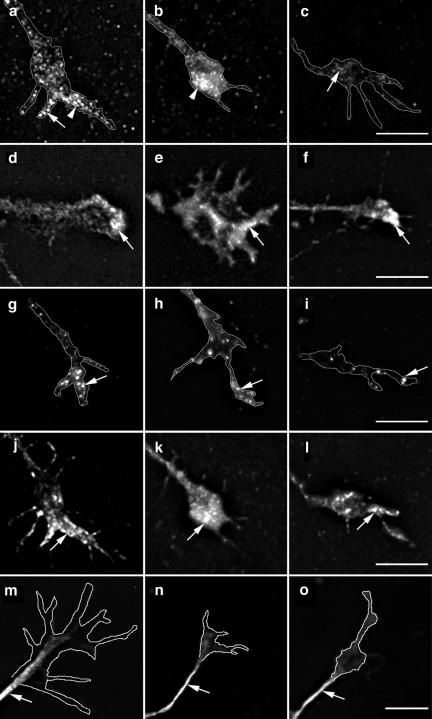
Figure 4.
Depletion of Mena from the growth cone plasma membrane in cells expressing inactive ARNO. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with myc-tagged ARNO wild-type and ARNO-E156K and labeled with anti-Mena antibody (a–c), anti-vinculin antibody (d–f), anti-ERM antibody (g–i), rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (j–l), or anti-β-tubulin antibody (m–o), and visualized by deconvolution microscopy. The left column shows growth cones of untransfected cells, the middle column shows growth cones of cells expressing ARNO wild-type, and the right column shows growth cones of cells expressing ARNO-E156K. All images were taken and processed using identical parameters. (a and b) In untransfected cells or cells expressing ARNO wild type, Mena is localized at the growth cone filopodia (arrow) and lamellipodia (arrowhead). (c) In the growth cone of a cell expressing ARNO-E156K, Mena is depleted from the growth cone (arrow). (d–f) Vinculin is localized at the distal region of the growth cone in all cells (arrow). (g–i) ERM proteins are localized at the growth cone filopodia (arrow). (j–l) F-actin is localized at the filopodial/lamellipodial extensions of growth cones (arrow). (m–o) β-Tubulin labeling is present in axonal shafts but not in the central domain of the growth cone. Growth cones have been outlined to facilitate the visualization of the distribution of labeling. Bars, 5 μm.