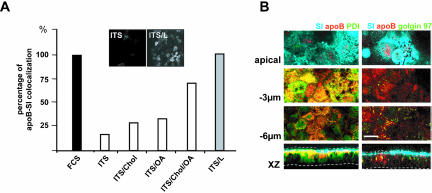
Figure 3.
Apical localization of apoB depends on lipid supply. (A) apoB-SI colocalization, as a function of basal lipid supply. In the basal compartment, ITS was used alone or supplemented with oleic acid (OA), cholesterol (Chol), or a mixture of OA, cholesterol, and palmitic acid (ITS/L). Confocal microscopy was used to study the colocalization of SI and apoB in each of these conditions. Results are expressed as the percentage of cells in which apoB and SI colocalized, with the value for cells incubated with FCS-supplemented medium set at 100%. Insets display XY acquisitions of the apoB signal in the apical region of cells cultured with ITS medium alone (ITS) or supplemented with lipids (ITS/L). (B) Immunolocalization of apoB (red channel), SI (blue channel), PDI (green channel on left panel), or Golgin 97 (green channel on right panel) at the apex, and at –3 and –6 μm with respect to the apical plane and in XZ representations in Caco-2 cells cultured in ITS medium. Dotted lines delimit the brush-border domain and the basal level of Caco-2 cells. Bar, 10 μm.